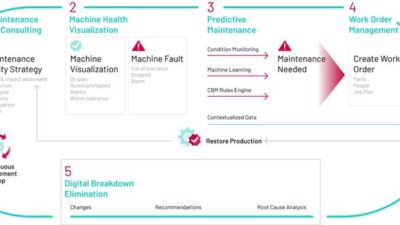
Maintenance best practices have evolved and are changing how workers stay safe and improve their operations.
Respondents
- John Gaddum, factory automation service manager, Bosch Rexroth, Hoffman Estates, Ill.
- Lance Gilbert, managing partner, Net Results Group, Louisville
- Pratibha Pillalamarri, senior product marketing manager, Aspen Technology, Houston

Question: What’s the current trend in maintenance for industrial and manufacturing facilities?
John Gaddum: The current trend for manufacturers is to rely more heavily on outsourcing of the expertise and knowledge of their equipment directly from the OEM’s or manufacturers (software / hardware) when there is a need.
Lance Gilbert: The current trend in maintenance for industrial and manufacturing facilities is leaning towards adopting software-as-a-service (SaaS) subscriptions for master data management (MDM). This approach acts as an upfront data governance tool that seamlessly integrates with enterprise resource planning (ERP), enterprise asset management (EAM) or computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS), ensuring efficient and standardized data management across operations.
Pratibha Pillalamarri: Manufacturing facilities are adopting data driven maintenance strategies by leveraging advancements in data analytics, Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and machine learning algorithms. This shift allows for real-time monitoring of equipment condition, enabling proactive identification of potential failures before they occur.
There is a growing emphasis on incorporating predictive maintenance into existing preventive maintenance programs to optimize maintenance schedules and resource allocation by considering equipment criticality & failure mode severity. The overall goal for asset intensive industries is to enhance equipment reliability, minimize downtime and maximize operational efficiency, driving down maintenance costs and improving productivity.
Question: What future trends should engineers, plant managers and designers expect for predictive and/or preventive maintenance in the next 1-2 years?
John Gaddum: Budgeting for transition and support planning. Transfer of budgeting from training their own employees, to the outsourcing of external experts with a plan in place to support the production demands of their equipment.
Lance Gilbert: in the next 1 to 2 years, engineers, plant managers and designers should anticipate a surge in future trends for predictive and preventive maintenance. This includes the widespread integration of artificial intelligence (AI), IoT, inspection technologies, digital twins, predictive analytics and the emergence of predictive-maintenance-as-a-service. Additionally, there also will be an increasing adoption of an array of immersive technologies on the shop floor, collectively shaping a tech-driven landscape to enhance maintenance strategies and overall operational efficiency.
Pratibha Pillalamarri: There’s a shift towards proactive, data-driven methods that aim at optimizing asset performance, reducing downtime, and promoting sustainability. Asset performance management (APM) solutions are crucial, offering comprehensive coverage of asset and process health. They aid sustainability efforts by minimizing downtime, product loss, resource and energy waste and expenses.
They also provide early warnings for process and mechanical issues, enabling timely adjustments to maintain yields and product quality. Predictive alerts facilitate proactive maintenance, avoiding unplanned breakdowns. APM solutions also promote sustainable practices, optimizing maintenance schedules and minimizing energy waste. This integrated approach enhances operational efficiency, reliability and environmental leadership in industrial and manufacturing sectors.
Question: What are the fundamental distinctions between predictive and preventive maintenance, and how do these approaches complement each other in an ideal maintenance strategy?
John Gaddum: Preventive maintenance is the time-tested practice of the scheduling of periodic maintenance in order to keep equipment from premature wear and tear. Preventive maintenance does not warn you, guarantee or prevent failures from occurring. It’s just good practice, similar to regular oil changes for your car, but certain electronic and mechanical hardware have a certain life expectancy. Predictive maintenance involves the monitoring of equipment, in real-time, to help identify or predict potential failures due to changes in the operation of equipment.
Lance Gilbert: The fundamental distinctions between predictive and preventive maintenance lie in their timing and approach. Predictive maintenance operates as needed, relying on real-time data collection and analysis of machine operation to detect issues at their early stages, preventing production interruptions. Repairs in predictive maintenance occur during machine operation, addressing actual problems.
In contrast, preventive maintenance involves scheduled routine inspections and tasks aimed at preventing potential issues. These approaches complement each other in an ideal maintenance strategy by combining proactive measures with just-in-time interventions. Predictive maintenance minimizes downtime by addressing issues precisely when needed, while preventive maintenance establishes a preventive framework to minimize the likelihood of issues arising in the first place. Together, they create a comprehensive strategy that maximizes equipment reliability and operational efficiency.
Pratibha Pillalamarri: Preventive maintenance involves regularly scheduled inspections, servicing and replacement of parts to prevent equipment failure. These tasks are calendar-based regardless of whether there are signs of impending failure. Predictive maintenance uses data from sensors and maintenance records and applies advanced analytics and other monitoring techniques to predict when equipment is likely to fail accurately. In an ideal world, these two strategies can complement each other. The data gathered from predictive maintenance can inform and refine the preventive maintenance schedule, ensuring tasks are performed when they’re most needed.
Predictive maintenance helps prioritize tasks based on actual equipment condition, while preventive maintenance ensures that essential maintenance tasks are not overlooked. By combining both approaches, organizations can allocate resources more efficiently.
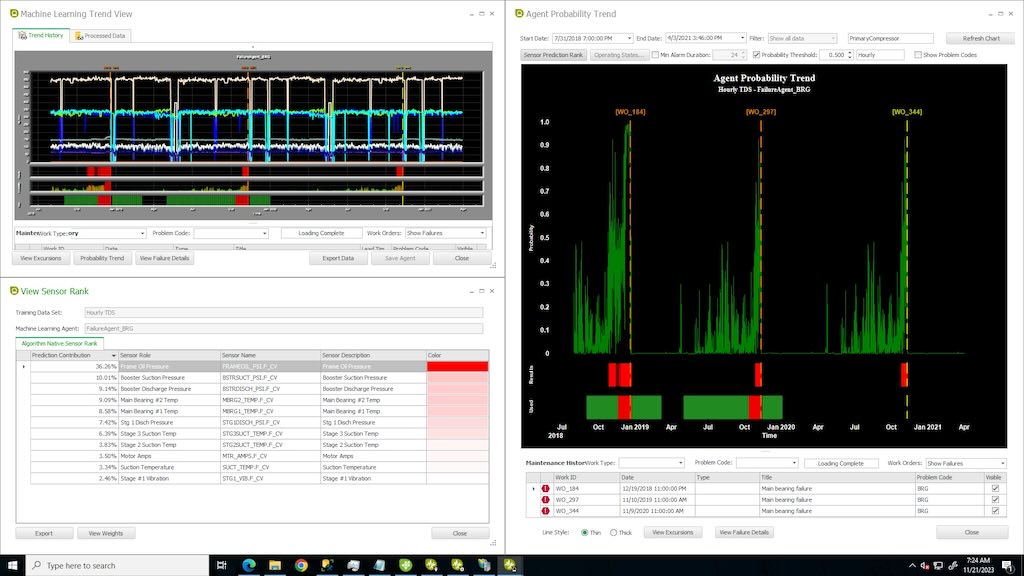
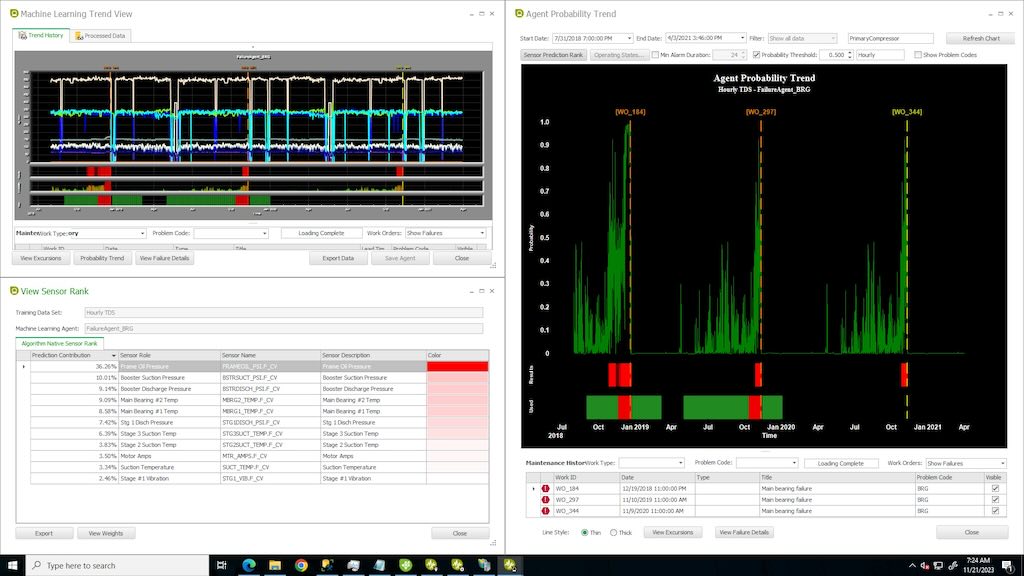
Question: Describe the successes from using programs that incorporate predictive, preventive, reliability-centered or reactive maintenance.
Lance Gilbert: Programs incorporating predictive, preventive, reliability-centered and reactive maintenance demonstrate success through systematic preventive schedules, efficient real-time interventions in predictive maintenance, optimized focus on critical components with reliability-centered approaches and swift issue resolution in reactive maintenance. This holistic strategy results in enhanced equipment reliability, prolonged asset lifespan and minimized downtime, contributing to improved operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Question: Tell us about a recent maintenance project you’ve worked on that’s innovative, large-scale or otherwise noteworthy. Please tell us about the location, plans your team engineered, key players, interesting challenges or solutions and other significant details.
Lance Gilbert: We recently led an innovative maintenance project within St. Gobain’s Building Products Division, collaborating closely with key stakeholders such as engineering and maintenance teams, inventory personnel and C-level executives.
The project aimed at achieving significant outcomes, including a remarkable 10% increase in maintenance productivity, a 12% improvement in machine downtime and a 10% boost in storeroom productivity. Our strategy also targeted enhanced PO accuracy and the elimination of 3-way match errors.
Despite an investment of $1.4 million, the project demonstrated exceptional efficiency, reaching break-even in nine months. The success of this large-scale initiative underscores our commitment to innovation, collaboration and tangible improvements in maintenance operations.
Question: What percentage of your team is focused on maintenance? What percentage of your entire operation is focused on maintenance? How will this change in the next 12 months?
John Gaddum: As part of the service group, our help desk and field service engineers are always supporting customer maintenance personnel, but not necessarily focused on predictive or preventive maintenance. We help guide customers on the practices but were more reactive to the causes of failure.
Lance Gilbert: As an MDM vendor, our entire team is dedicated to maintenance and inventory levels, constituting 100% of our focus. Our operational structure revolves entirely around providing comprehensive solutions in these domains.
Looking ahead, over the next 12 months, our commitment to maintenance and inventory management remains steadfast, with no anticipated changes in our strategic focus. We continue to prioritize excellence in MDM services to further support our clients in optimizing their maintenance operations and enhancing overall efficiency.
Question: What are the leading causes of unscheduled downtime, and how do you overcome these?
John Gaddum: Not having any predictive or preventive maintenance plan. We see this a lot at our customers when their production overrides the need for taking good care of the equipment.
Lance Gilbert: The leading causes of unscheduled downtime often include not having the right part at the right time, missing or incomplete bill of materials (BOM) parts lists, an excessive number of emergency orders and spot buys, and unplanned outages exceeding acceptable tolerances. These challenges can be effectively addressed through the implementation of a robust MDM system.
By centralizing and managing critical data related to parts, inventory and maintenance processes, an MDM system ensures accurate and up-to-date information, minimizes errors in BOMs, optimizes inventory levels and streamlines the procurement process. A well-implemented MDM system becomes a proactive solution to mitigate the causes of unscheduled downtime, promoting operational efficiency and reducing disruptions.
Question: What new or increased technologies do you plan to implement at your facility?
Lance Gilbert: We recommend a comprehensive MDM platform. This platform will encompass software solutions, a robust data dictionary, integration with EAM and a SaaS model. Additionally, we aim to incorporate services and reliability information into the MDM framework. This approach harnesses the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning, streamlining data management processes, enhancing system reliability, and ultimately contributing to the overall success of any facilities that deploy.
How have artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) changed maintenance in the last few years and what have the results been like?
Pratibha Pillalamarri: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have transformed maintenance practices, enabling predictive and prescriptive approaches. By analyzing data from sensors, equipment logs and historical records, these technologies predict equipment failures, optimizing maintenance schedules based on actual condition rather than predetermined time intervals. This minimizes downtime and maximizes asset performance. Integrating AI and ML can yield significant results such as reduced unplanned downtime, improved reliability, and enhanced efficiency. These technologies can extend equipment lifespan, cut maintenance costs, and enhance asset management strategies. They also can facilitate the shift from reactive to proactive maintenance, improving resource allocation and productivity. As AI and ML evolve, their impact on maintenance is expected to grow, driving further improvements in reliability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness across industries.

Question: What tips would you offer to someone newly tasked with maintenance duties?
John Gaddum: Put a preventive and predictive plan in place and plan to provide remote access to your equipment from reliable resources for support.
Lance Gilbert: For someone newly tasked with maintenance duties, my key tip would be to thoroughly examine the need for implementing an MDM system at your plant. A robust MDM system can significantly streamline maintenance operations by centralizing and maintaining accurate data related to assets, parts and maintenance processes. It enhances data reliability, reduces errors, and ensures consistency across various systems. By adopting MDM early on, you establish a strong foundation for effective maintenance management, ultimately contributing to increased operational efficiency and improved decision-making.