Personal protective equipment (PPE) plays a pivotal role in ensuring worker safety across various industries. Nine future PPE trends in manufacturing are highlighted
Learning Objectives
- Gain a comprehensive understanding of the importance of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) in safeguarding workers from workplace hazards.
- Get familiar with key industry regulations and standards governing PPE selection and compliance, ensuring worker safety and legal adherence.
- Acquire insights into best practices for conducting comprehensive risk assessments, balancing cost-effectiveness with safety and effectively sourcing PPE to enhance workplace safety and overall operational efficiency.
PPE insights
- Choosing the right PPE is beyond compliance; it’s safeguarding lives. Identifying hazards, adhering to industry standards, and balancing costs ensure comprehensive protection.
- PPE regulations aren’t universal. Compliance isn’t just legal; it’s a commitment to safety. Regional variations and evolving standards necessitate continuous monitoring.
- The future of PPE transcends traditional gear. From IoT-integrated equipment to AI-driven risk assessment, innovations prioritize worker well-being and operational efficiency.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is a universal foundation of safety in facilities. It’s not merely a compliance hurdle — PPE represents an organization’s dedication to the well-being of its workforce. In industries where risks are inherent, the right PPE can mean the difference between a regular workday and a life-altering incident.
Plant managers face a number of challenges when it comes to PPE. The task isn’t just about finding equipment, but also finding the right equipment that meets industry standards, suits specific task requirements and fits budgetary constraints. Ensuring quality and timely delivery adds another layer of complexity.
Understanding the basics of PPE
PPE serves a singular, vital purpose: to shield workers from workplace hazards. It’s a barrier that mitigates the risk of injury or health complications arising from specific job functions or environments. Whether it’s protection from chemicals, electrical currents or physical impacts, PPE ensures workers return home in the same health they arrived in.
The spectrum of PPE is vast, tailored to the myriad risks workers might encounter. Headgear protects against falling objects, while specialized footwear might offer resistance against electrical hazards or chemical spills. Each piece of equipment is designed with a specific threat in mind, ensuring comprehensive protection.
In specialized areas like electrical, mechanical, and automation engineering, PPE takes on heightened significance. Electrical engineers, for instance, need PPE that guards against electrical shocks and arcs. Mechanical engineers might require protection from moving parts, while those in automation need safeguards against the unique risks posed by automated machinery. In maintenance and management, PPE ensures that routine checks and repairs can be conducted safely, without exposing workers to undue risks.
Industry regulations’ role in PPE selection
Industry regulations form PPE standards, ensuring that equipment meets specific safety criteria. These regulations, often developed by industry experts and safety organizations, provide a benchmark for PPE quality and performance.
Among the most prominent regulation in force today includes:
-
OSHA Standards (U.S.): The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets and enforces standards to ensure safe working conditions for employees in the U.S. Its regulations cover a wide range of PPE including eye and face protection, respiratory devices, and protective clothing.
-
Personal Protective Equipment at Work Regulations (UK): This UK-specific regulation mandates employers to provide appropriate PPE for their workers. It covers the assessment, provision, maintenance, and correct use of PPE to protect workers from health and safety risks.
-
PPE Regulation (EU) 2016/425 (European Union): This EU regulation outlines the requirements for PPE design, production, and marketing to ensure a high level of protection for users. It emphasizes the responsibilities of manufacturers, importers, and distributors.
-
ANSI/ISEA Z87.1 (U.S.): Defined by the American National Standards Institute and the International Safety Equipment Association, this standard pertains to the requirements for eye and face protection devices, ensuring they provide adequate protection against specific hazards.
-
AS/NZS 2210.1 (Australia/New Zealand): This standard, set by the joint Australian/New Zealand committee, focuses on safety, protective, and occupational footwear. It ensures footwear meets specific requirements to protect against various workplace hazards.
-
CSA Standard Z94.3 (Canada): The Canadian Standards Association’s regulation for eye and face protectors. It outlines criteria related to the design, construction, testing, and use of eye and face protection devices.
-
NFPA 70E (U.S.): Developed by the National Fire Protection Association, this standard addresses electrical safety-related work practices. It provides guidance on PPE selection for workers exposed to electrical hazards.
-
ISO 20345 — Safety Footwear (International): An international standard set by the International Organization for Standardization, ISO 20345 specifies requirements for safety footwear, ensuring protection against various risks like impact, compression, and chemical exposure.
Compliance with PPE regulations isn’t just a matter of legality, but a commitment to worker safety. Non-compliance can lead to severe repercussions, both in terms of worker health and legal consequences. Beyond the immediate risk of injuries or fatalities, organizations might face hefty fines, lawsuits, and reputational damage if they fail to adhere to established standards.
Another important consideration: PPE regulations are not one-size-fits-all. They vary based on the specific risks associated with different industries and are often tailored to address those unique challenges.
Regional differences also come into play with countries or even states having their own sets of rules based on local risks, industry presence, and historical data.
Conducting comprehensive risk assessments
Conducting a risk assessment is a systematic process. It begins with identifying potential hazards in the workplace, whether they’re related to machinery, chemicals, or processes. Once identified, these hazards are evaluated based on their likelihood and potential severity. Finally, appropriate measures, including the selection of suitable PPE, are implemented to mitigate these risks.
Different manufacturing areas come with their own set of challenges. For instance, the assembly line might pose risks related to moving machinery, while the chemical processing unit could expose workers to toxic substances. It’s crucial for plant managers to dissect each area, understand the specific hazards present, and ensure that workers are adequately protected.
Once hazards are identified and evaluated, the next step is to determine the appropriate PPE. This decision is based on the risk level associated with each hazard. For high-risk scenarios, PPE with rigorous protective features might be required, while lower-risk environments might necessitate more basic protection.
Balancing cost-effectiveness with safety considerations
While the upfront cost of PPE is a tangible figure, plant managers must also consider the potential costs of skimping on protection. Non-compliance or accidents can lead to financial liabilities far exceeding the initial investment in quality PPE. It’s important to view PPE not just as an expense but as an investment in safety and long-term financial prudence.
The lifespan of PPE is a crucial factor in its overall cost-effectiveness. Durable equipment that can withstand the rigors of daily use without frequent replacements offers better value in the long run. Regular maintenance checks ensure PPE remains in optimal condition, maximizing its protective capabilities and lifespan.
Balancing safety and budgetary constraints requires a strategic approach. This might involve bulk purchasing, negotiating with suppliers for better rates, or investing in durable PPE that, while more expensive initially, offers longer service life and better protection. Regular maintenance and timely replacement also can ensure PPE remains effective without incurring unnecessary replacement costs.
Best practices and recommendations for sourcing PPE
Identifying the right PPE supplier is almost as crucial as selecting the right equipment. Managers should seek suppliers with a proven track record, verified testimonials, and industry certifications. Engaging in pilot testing or requesting samples can also provide insights into product quality before making a bulk purchase.
Quality assurance is non-negotiable when it comes to PPE. Given the critical role PPE plays in worker safety, ensuring that products meet or exceed industry standards is paramount. Regular audits, third-party certifications, and adherence to international safety standards can provide confidence in a supplier’s product quality.
Local sourcing often offers faster delivery times and easier communication, but it may come with a higher price tag. International suppliers, on the other hand, might offer competitive prices but could pose challenges in terms of shipping delays, customs issues, or quality inconsistencies. Weighing these pros and cons based on specific needs can guide the sourcing decision.
Bulk purchasing can lead to significant cost savings, as many suppliers offer discounts for large orders. Forming partnerships or joining consortiums also can provide collective bargaining power, leading to better pricing and terms. These strategies not only reduce costs, but also can streamline the sourcing process.
Implementing PPE protocols and training
Even the best PPE can fail if not used correctly. Comprehensive training ensures that staff understand the importance of PPE, know how to wear and maintain it, and are aware of its limitations. Regular refresher courses can reinforce this knowledge, ensuring consistent and correct PPE usage across the board.
Routine checks and maintenance are vital to ensure PPE remains in optimal condition. Protocols should be established for regular inspections, cleaning, and, if necessary, replacements. Such proactive measures can prevent equipment failures and ensure workers are protected at all times.
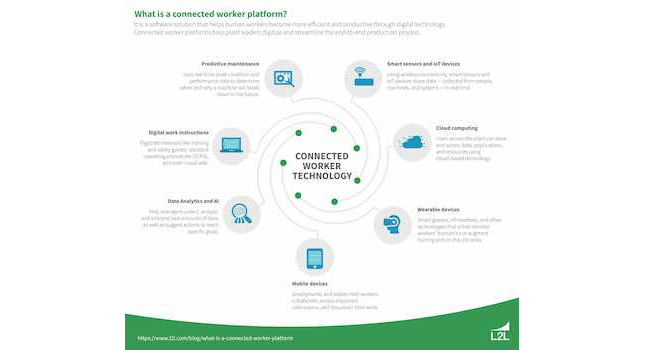
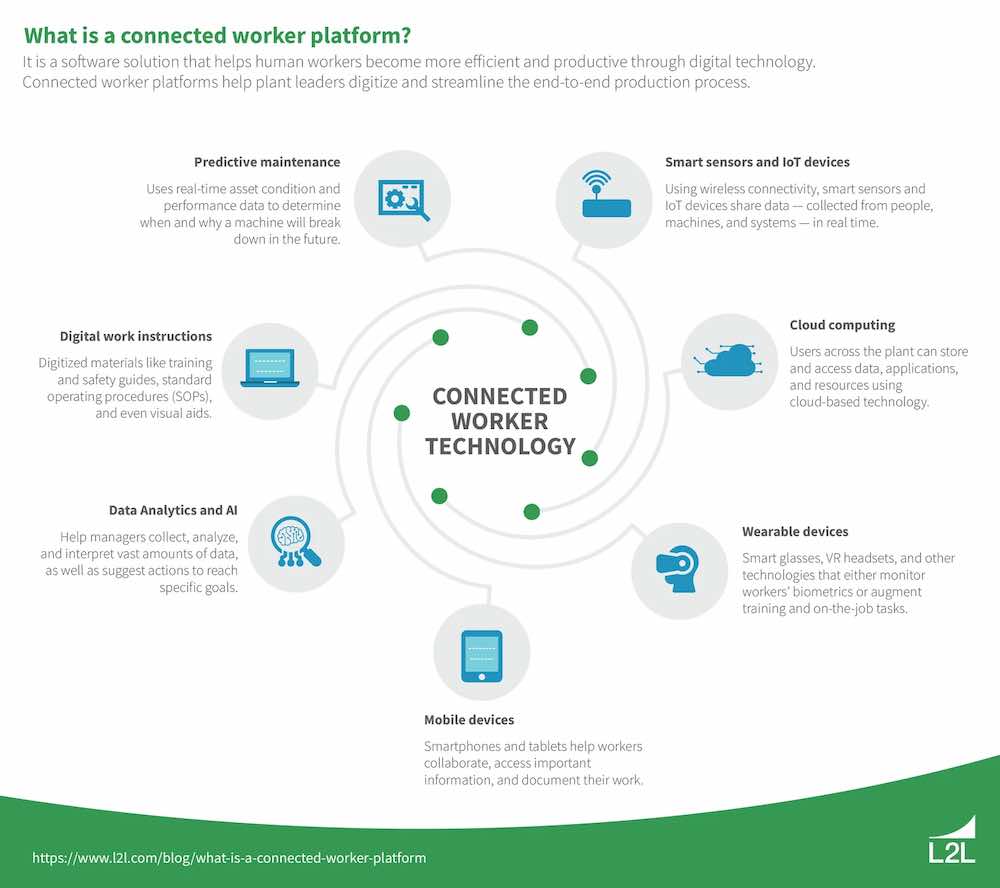
Connected worker platforms, leveraging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), can further enhance PPE management. These platforms can monitor PPE usage, send alerts for maintenance or replacement, and even provide data-driven insights to improve safety protocols. Integrating such technologies can elevate the effectiveness of PPE programs.
Nine future PPE trends in the manufacturing sector
The PPE industry, like many others, is undergoing a transformation driven by rapid technological advancements. Innovations like smart helmets with augmented reality or wearables that monitor vital signs are reshaping the PPE landscape. These advancements not only offer better protection, but also enhance worker efficiency and comfort.
Let’s look into some exciting trends to watch out for in the near future (some of which are already being implemented):
-
Work exoskeletons: Work exoskeletons are wearable devices that amplify a person’s physical capabilities by providing external support and augmentation, allowing them to lift heavy objects with minimal effort and reducing the risk of musculoskeletal injuries. These devices reduce the risk of musculoskeletal injuries, helping ensure workers can perform physically demanding tasks without compromising their health.
-
Smart fabrics: Smart fabrics represent the next frontier in adaptive wearables. These advanced textiles come embedded with sensors that can detect and respond to environmental conditions. Whether it’s regulating temperature to keep workers comfortable or changing texture to provide better grip, smart fabrics are set to redefine how we think about clothing in the workplace.
-
IoT-integrated PPE: The fusion of IoT with PPE is a game-changer. Such equipment can continuously send real-time data about its condition, wear, and tear. This ensures timely maintenance or replacement and provides insights into environmental conditions, alerting workers to potential hazards in their vicinity.
-
Drones for safety inspections: Drones are revolutionizing safety inspections. They can swiftly and safely inspect hard-to-reach or potentially hazardous areas, ensuring environments are safe before workers set foot in them. This enhances safety while saving time and resources at the same time.
-
AI-powered risk assessment tools: Predictive tools use AI to analyze vast amounts of data to foresee potential hazards, allowing for proactive safety measures. These tools can recommend tailored PPE solutions based on specific tasks, environments, and individual worker profiles.
-
Virtual reality (VR) training: VR can simulate a range of hazardous situations, allowing workers to practice safety protocols in a risk-free environment. This immersive training helps ensure workers are prepared and know the right actions to take when faced with real-world dangers.
-
Biometric monitoring wearables: Health monitoring goes beyond the doctor’s office with these wearables. Devices that continuously monitor vital signs, fatigue levels, and other health indicators can provide real-time feedback to workers. If any anomalies are detected, alerts can be sent to both the worker and supervisors, ensuring timely interventions and reducing health risks.
-
Augmented reality (AR) maintenance guides: Wearable AR devices can overlay digital information on the physical world, providing real-time guidance on equipment maintenance and repair. This ensures tasks are performed safely, efficiently, and correctly, reducing the risk of equipment malfunctions.
-
Environment-sensing devices: These devices are like a sixth sense for workers. Wearables equipped to detect harmful gases, radiation, or extreme temperatures can provide immediate alerts. By doing so, they ensure workers can take timely precautions, avoiding exposure to potentially harmful conditions.
Keep in mind that as industries evolve, so do the risks associated with them. This will lead to changes in PPE regulations and standards. Plant managers should stay on top of industry trends, participate in relevant forums and engage with regulatory bodies to anticipate and prepare for these shifts.
Continuous learning and adaptability are key for plant managers. Subscribing to industry journals, attending seminars, and participating in workshops can provide insights into emerging risks and PPE solutions. Building a network of peers and experts also can offer a platform for knowledge exchange and collaboration.
Developing a strong PPE approach
An informed approach to PPE is the bedrock of worker safety. Aside from buying the equipment, it’s about understanding the unique risks of an environment and sourcing the best protective solutions. With the right strategies and a proactive mindset, plant managers can ensure their teams are not only protected, but empowered to perform their best.



