To support digital transformation, plant leaders must modernize the network infrastructure, yet ensure it remains flexible and secure.
Advanced SD-WAN insights
- Advanced software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) can help five common use cases such as connecting remote manufacturing facilities, reducing equipment sprawl, accelerate disaster recovery and securing IIoT with a zero-trust network.
- To support digital transformation, plants must modernize their network infrastructure, while maintaining its flexibility and security.
The manufacturing industry has been through a time of huge change and now is transitioning to a post-lockdown world. All the changes in workforce and shifts in consumer needs have led to labor shortages and unpredictable availability of goods and transportation, leading to supply chain disruptions. Now, it’s crucial for plant engineers to step back and reconsider their approaches and find new ways to leverage technology, such as advanced software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN). One objective is to automate as much as possible to reduce the impact of disruptions on existing and future production.
Central to digital transformation should be a focus on key technologies, including the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), artificial intelligence (AI) and advanced robotics. Each of these requires robust connectivity and IT agility, aimed at creating smart factory environments and re-imagined business processes that can provide the edge necessary to thrive midst uncertainty.
Automation is top of mind, especially as a recent Gartner survey found that 57% of manufacturing leaders feel their organization lacks skilled workers to support smart manufacturing digitization plans, further squeezing plant managers who must do more with fewer workers, despite spiking demand.
However, with an increased reliance upon IIoT devices, plant leaders must also consider the state of their security, and their capability to contend with a growing cyberattack surface area, exposing their respective plant environments to a rising tide of cybersecurity risks that would have been unimaginable just a generation ago.
Software-defined wide area networks hold the key to digital transformation
The shift to digitizing the plant environment, known as digital transformation, has placed tremendous pressure on legacy information technology systems, especially the network. Today, plant environments must have a dependable and secure network that traditional router-based network architectures can no longer provide. Here, an advanced SD-WAN solution can help plants tackle five common use cases that will both reduce cybersecurity risks while ensuring the organization takes full advantage of its respective automation investments.
1. Connect remote manufacturing facilities with advanced SD-WAN
Organizations that operate internationally with factories and plants dotting the globe must manage the potential of poor connectivity as a result of multiple remote locations. To connect these remote sites, manufacturers often subscribe to MPLS lines, but these services are expensive while offering limited bandwidth nor the flexibility to scale with the business, reducing the overall quality of service and network performance. Remote locations also experience jitter and packet loss affecting real-time applications, such as VoIP and video conferencing, let alone IIoT devices critical to plant operations.
Here, an advanced SD-WAN solution can deliver improved network performance and connectivity by complementing – and even replacing – an MPLS line with broadband internet and 5G/LTE connections, while also providing flexibility and reduced costs. SD-WAN can help deliver comparable performance as private lines over broadband internet and 5G/LTE connections using techniques, such as path conditioning that can rebuild lost packets at destination.
2. Reducing equipment sprawl while standing up new sites quickly
As the organization grows, leadership must often connect new plant environments and facilities to the broader corporate network. Furthermore, as organizations improve automation and integrate new technology, they must also integrate third party suppliers or other key stakeholders. This all must be completed and deployed quickly to match the speed of the business, but a new MPLS line can take 60 to 120 days to provision and configure, whereas, broadband services can be installed in just a few days, though requiring experienced local staff.
With advanced SD-WAN, staff and support teams can stand up a new site within a few minutes using existing internet or 5G connections. Such a program can also use zero-touch provisioning, meaning the need to send experienced IT staff onsite to complete the rollout is no longer necessary. Remotely, staff can ensure security policies are seamlessly enforced at the new location and that any policy changes can be automatically distributed to potentially thousands of locations in minutes. From a security perspective, advanced SD-WAN can also integrate routing, firewall, and other WAN optimization capabilities that reduces the need to stack multiple networking devices at remote locations, eliminating complexity and equipment sprawl that can become difficult to manage and provision.
3. Accelerate disaster recovery with advanced SD-WAN
For organizations with plants connected across the globe, the organization is subject to network latency. Plant personnel often have large files to transmit to remote sites, such as engineering CAD files, but the transfer can take a long time or fail to transmit due to latency issues, especially when dealing with remote sites.
In addition, manufacturers regularly perform backups at remote sites for disaster recovery purposes. To overcome the effects of latency, advanced SD-WAN programs can accelerate the transmission of data by applying transmission control protocol (TCP) acceleration and data reduction.
4. Moving and securing applications and traffic in the cloud with SASE
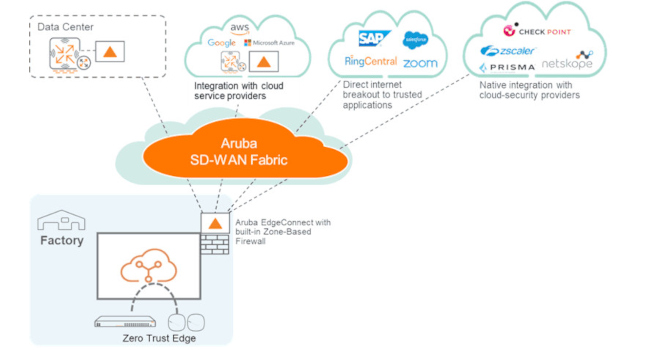
Similar to the rest of the business world, plant environments are also increasingly leveraging cloud environments to host critical business applications, diminishing the role of the traditional data center. With this shift, it is no longer relevant to backhaul the traffic to the data center, as it can negatively affect application performance. Rather, cloud traffic can be steered to a point or location closer to the user to help reduce latency while increasing application performance via the cloud.
Additionally, with hybrid work becoming the norm, even in plant environments, remote workers via SD-WAN can connect from anywhere and access sensitive data in the cloud as if they were in the plant. This convenience, however, also requires an additional layer of cloud-based security enforcement. In response, IT teams can leverage a Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) architecture, paired with an advanced SD-WAN vendor, to ensure a robust IT security paradigm no matter where and how data is accessed and transmitted.
For example, advanced SD-WAN can help steer traffic intelligently based on quality-of-service requirements and security policies. Traffic from trusted cloud applications, such as Microsoft 365 may be sent directly to the cloud, freeing up bandwidth for traffic that must be routed through the data center. Traffic from untrusted or unknown applications can be first sent to the cloud-delivered security services for further security inspection before forwarding to the cloud, as part of a robust SASE architecture.
Advanced SD-WAN enables manufacturers to build a best-of-breed SASE architecture without compromising security functions through a tight integration with multiple cloud-security vendors offering capabilities, such as ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access), CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker) and SWG (Secure Web Gateway).

5. Secure IIoT with a zero-trust network
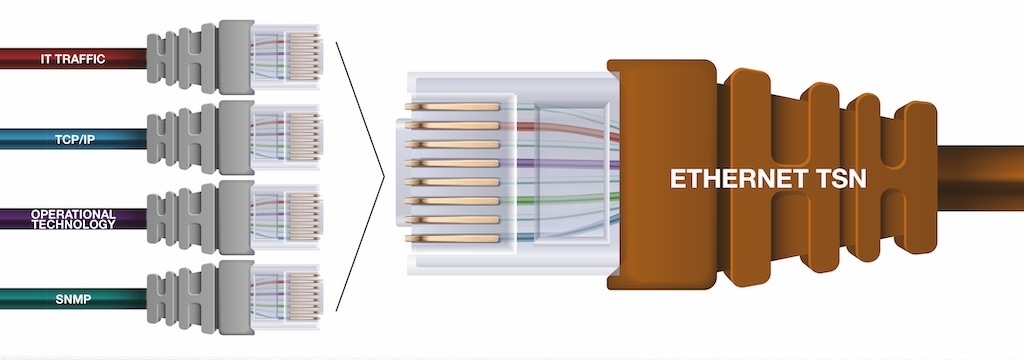
With the rise of plant automation comes a tidal wave of IIoT devices, both improving plant operations but also greatly expanding the attach surface. For one, IIoT devices are difficult to secure as they usually cannot host a security agent and often lack authentication systems. Another concern is the convergence of IT and OT (operational technology). In the past, IT and OT networks used to be separated, but a new generation of OT devices is now connected to the IT network to feed IT systems with data from a variety of sensors on the plant floor. This trend dramatically increases cybersecurity risks as malware can spread from unsecured OT devices to the IT network.
An advanced SD-WAN with zero-trust segmentation capabilities can help segregate and better protect the network. By separating the networks into subnetworks via SD-WAN, IT can better limit the spread of cyberattacks and malware from infecting other parts of the network. IT also can go a step further by adding identity and role-based access control to better manage network access while enabling automated dynamic segmentation. Furthermore, advanced SD-WAN capabilities might include an embedded firewall with built-in signature-based intrusion detection and prevention capabilities (IDS/IPS) to monitor and protect the network for malicious activities or policy violations.
Future-proofing the plant environment
Within challenging times from supply chain disruptions to labor shortages, manufacturers and other plant environments must accelerate digital transformation. To support this transformation, plant leaders must modernize the network infrastructure, yet ensure it remains flexible and secure. Advanced SD-WAN solutions can provide the foundation for smart manufacturing and flexible connectivity by virtualizing network links and providing private-line-like performance over the internet and wireless connections. It is a key component to ensure advanced security such as zero-trust segmentation. Additionally, the SD-WAN solutions must seamlessly integrate with multiple leading cloud security capabilities so manufacturers can build a best-of-breed SASE architecture that fits their business and security objectives.