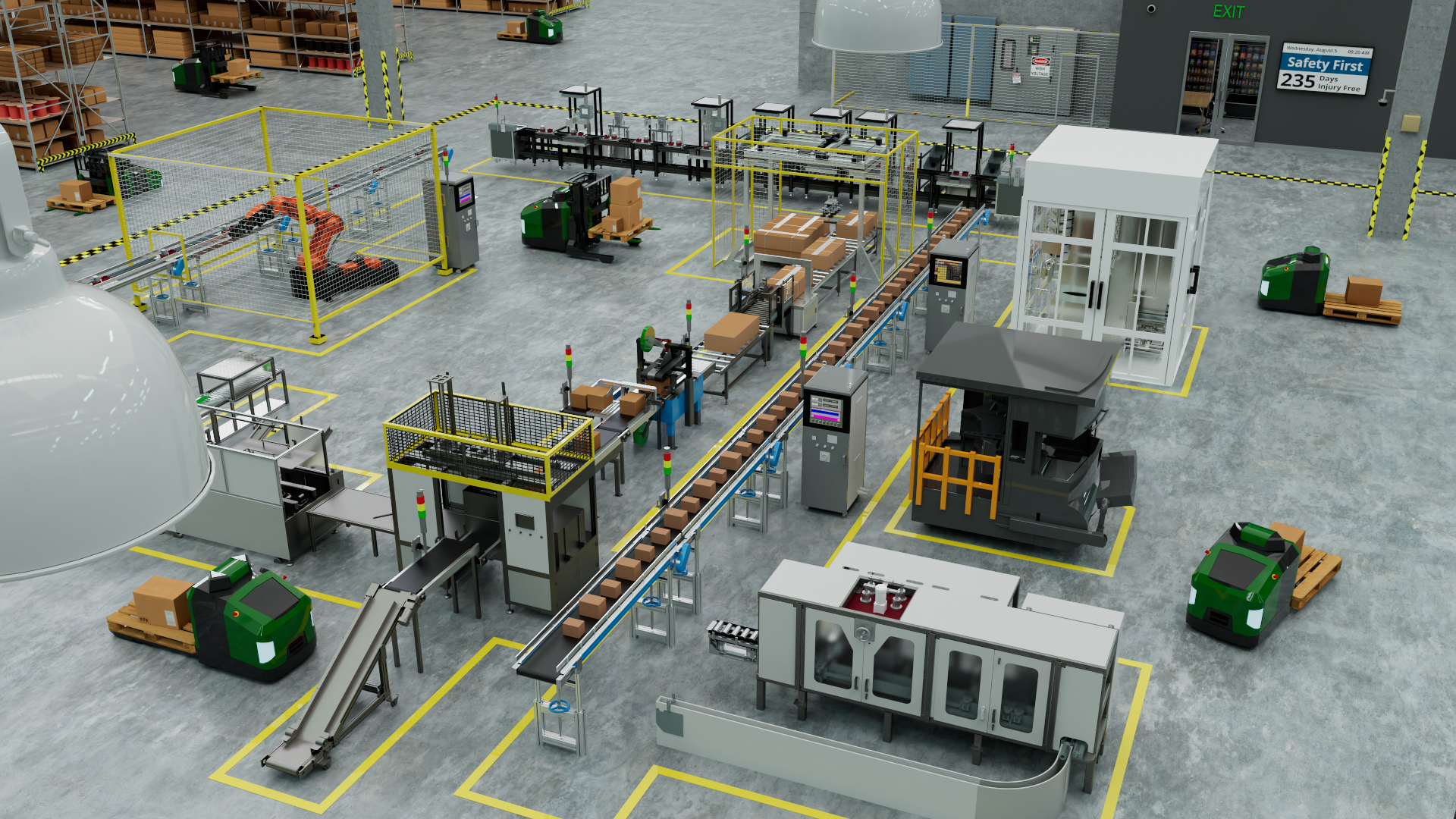
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) can improve productivity and output, but they do have limits manufacturers should be aware of.

Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are often conceived as machines used to transport heavy materials within facilities, factories, or warehouses. While this is true, AGVs have been integrated into a variety of industries outside of distribution and manufacturing, including retail, military and even healthcare.
With the growing popularity of AGV vehicles, many business owners and operations managers want to know if AGVs are a suitable fit for their company as they automate their warehouses or distribution centers.
Five advantages of AGVs
AGVs are not suitable for every business or set of operations but when they are suitable, they can bring a lot of benefits. Here are some of the key advantages of using AGVs.
1. Reduced labor costs
When a company installs an AGV, it is a one-time investment that can last up to a year with minimal maintenance. AGVs can work long hours and help companies save money on labor in a variety of ways. A company pays a single expense for the equipment – the initial investment – rather than the continuous costs associated with a new hiring, such as health insurance, salary increase, payroll taxes, vacation time, etc.
2. Increased safety
AGVs are designed with safety in mind. They have dedicated tracks they move on and don’t cross operator pathways. They also can be controlled using wearables. This reduces the possibility of human error when material handling systems are operating.
On the other hand, human-operated equipment, such as forklifts, lack many built-in safety features and is reliant on human input, which can be compromised in a variety of ways. Compared to a human operator, who is always at risk of becoming distracted or exhausted causing an accident, AGVs pose no such risk.
AGVs also can function in settings that humans are either unable to operate in such as excessive heat or cold or in the presence of dangerous materials. Enhanced safety levels lead to lower costs and less downtime, which can help many businesses increase their profitability.
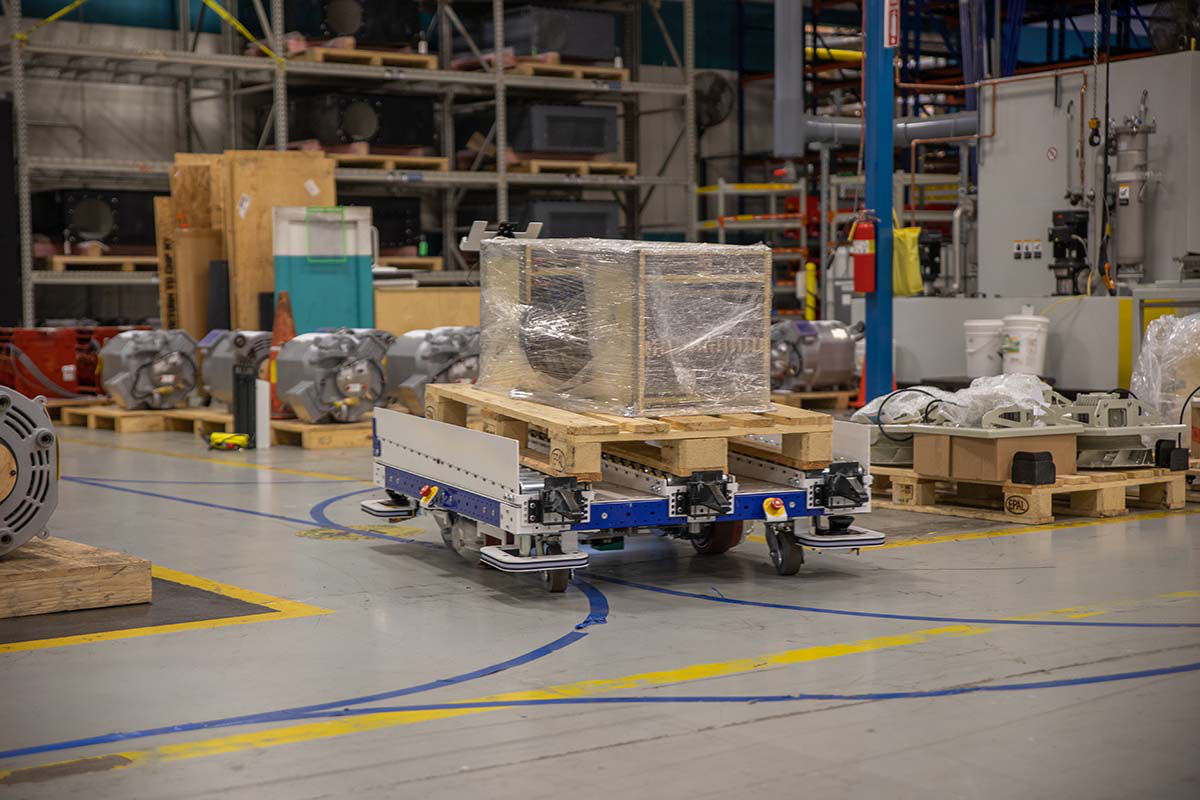

3. Increased productivity and output
AGVs benefits such as lower direct labor costs, less indirect costs, and errors, and improved safety conditions contribute to higher overall productivity. Unlike humans, AGVs do not get tired or distracted, do not have to take breaks, and can work 24 hours a day, seven days a week. AGVs are configured to take the most efficient route or complete a specific task. If a business operates on two shifts, management might consider rethinking operations and performing tasks during an “automatic” extra night shift.
Managers also can streamline operations such as inventory and material ordering by connecting AGVs to a warehouse control system or a warehouse management system
4. Increased accuracy
People make mistakes. AGVs are configured to take the most efficient route or complete a particular task. By replacing humans with AGVs, companies can eliminate some of the risks of workflow inaccuracies. Automation allows companies to make processes more productive and accurate by reducing waste and increasing total production.
5. Increased modularity/scalability
In comparison to fixed equipment, AGVs are simple to scale. As the business grows, management can add more AGVs as needed.
Although scalability can be achieved with manual vehicles, this is not a significant advantage. Compared to fixed equipment, AGVs are much more scalable. Instead of acquiring a large fixed conveyor (for example), AGVs allow you to start with just a few AGVs and expand the fleet as customer demand grows. Companies can boost system production by adding additional AGVs without having to do any physical work.
Five disadvantages of AGVs
Even though it seems like AGVs could be used in almost every industry, there are some potential drawbacks companies need to consider.
1. High initial costs
AGVs improve an operation’s bottom line by lowering labor expenses and boosting productivity, but they come at a cost: The initial investment. In the short term, purchasing an AGV will almost definitely be more expensive than employing people or using other equipment like a forklift. Savings are obtained over a long period of time. For smaller businesses that don’t have easy access to finance, this can make an AGV too expensive.
2. Increased maintenance cost
AGVs, like any other machine, requires normal maintenance and repair. Even if AGVs are not directly operated by employees, there will be downtime while employees are trained, and AGVs are introduced. To troubleshoot the AGVs, you’ll need a technical assistant. The cost of covering occasional expenses should be considered, as more potential will be needed.
3. Decreased flexibility
It is important to know AGVs have fixed movement routes and cannot flee if something is in their way. If the AGV vehicle, for example, comes across an obstacle in its path, it will come to a halt and wait until the road is clear. There will always be a need for human intervention. It is essential the control room monitoring the AGV is prepared to intervene if it is halted by an obstacle. To limit these kinds of situations, ensure AGV pathways are clear and don’t collide.

4. Unsuitable for non-repetitive tasks
The hardware is programmed to repeat the same task for an equal amount of time, but if the task is changed under certain conditions, the AGV’s programmed for a specific function cannot be used unless the software is changed. This is a major disadvantage, and the entire manufacturing unit will be shut down.
If operations are not repetitive, personnel operating different equipment might complete them faster and more efficiently (like as a forklift). AGVs may not be the ideal solution for a business plan that reacts to trends or is otherwise dynamic.
5. More vulnerable with virtual connectivity
Companies can substitute operators on short notice with a manual system. If a forklift driver is unavailable, they can find a trained replacement operator to cover the void until the forklift driver is available again. If there is a problem with an AGV, the unit must be taken out of operation until the problem is identified and fixed.
AGVs are complicated machines with many sensors and software designed to regulate their functions. Getting them repaired or replaced can take a long time. This is especially true if the device is highly-customized and specialized.
Having out-of-service assets for a long time can have a negative impact on production and profitability. Mechanical difficulties can often be resolved by replacing parts, but software or sensor issues can be more difficult to diagnose and repair. Regular software upgrades increase performance and boost diagnostic functionality.
AGV pros outweigh the cons
The advantages and disadvantages of AGVs are numerous, but the decision to invest in AGV technological infrastructure must be carefully considered.
Every company is different. Whether an AGV solution is the optimum investment for your company depends on the size of your operation and the working environment.
Many downsides of using an AGV are temporary. Although the initial investment is high, the returns are higher in terms of efficiency and maintenance costs. As technology advances, AGVs are becoming more efficient and responsive to changes in the operational route.