Learn the STAMPED method, which provides valve selection guidance
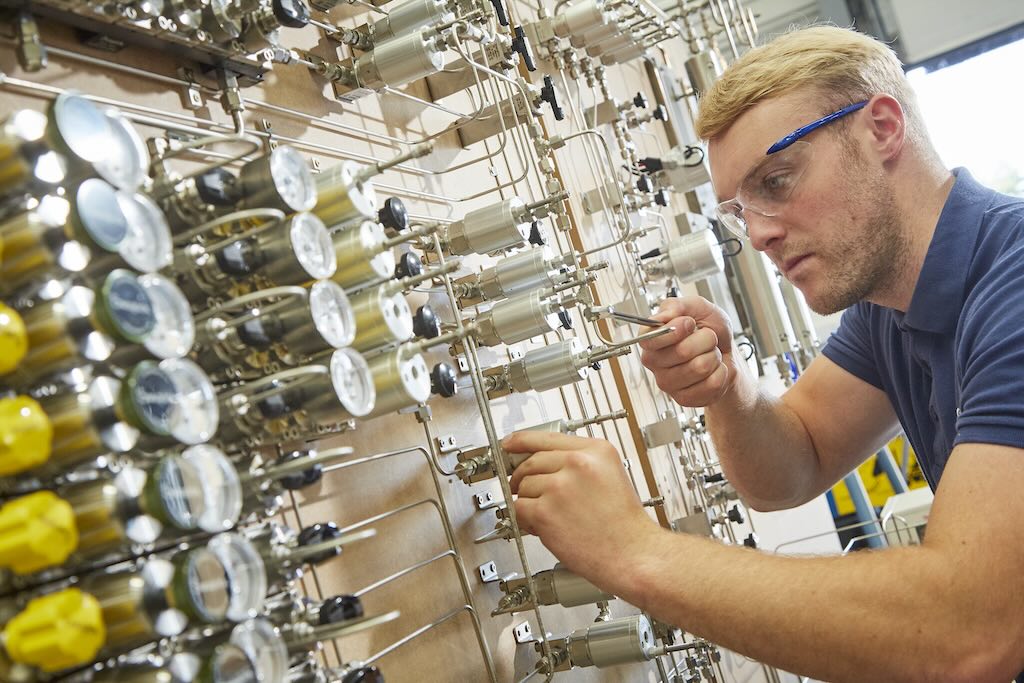
Whether you need a relief valve or other type of fluid system valve, a variety of considerations abound when making a selection. You want to get that selection right, as choosing an improper valve could lead to avoidable safety risks, poor performance and even increased downtime (see Figure 4).
A helpful tool when choosing a valve for your system is the STAMPED method, which stands for size, temperature, application, media, pressure, ends (or fittings) and delivery. This method provides a framework to help fluid system designers pick the proper valve and entails:
-
Size: The size of valve to use is dependent on the required flow rate needed for the system to operate as intended. Choose a valve that makes that rate possible by consulting the manufacturer’s published flow coefficient (Cv). This data shows the relationship between the pressure drop across a valve and the resulting flow rate. A reputable supplier should be able to provide guidance on the right-sized valve for the situation. Some even offer a Cv calculator to help.
-
Temperature: The temperature at which the valve will be operating is also important to know, as well as whether that temperature will be constant or fluctuate, to ensure compatibility. That includes both the temperature of the media the valve will control as well as the ambient operating temperature of the environment. Temperature fluctuations can cause seals to expand and contract, causing rapid wear that may lead to failures and leaks.
-
Application: System designers must know the specific function of a valve to make the right selection. In the case of a relief valve, it will need to allow the system to release pressure to avoid overpressurization. Other valves may need to start or stop flow or perhaps regulate flow levels instead. For example, most two-way ball valves only allow for on/off operation, so if the system needs to throttle or regulate flow, a needle or metering valve would be a better choice.
-
Media: Compatibility with system media and the ambient environment is key for a valve to operate as expected. All materials of construction, including bodies, seats, stem tips and other softer materials, must be compatible since valves are made from a variety of materials. Otherwise, corrosion, embrittlement or cracking may occur.
-
Pressure: Pressure limitations are determined by the lowest-rated component in a system, with valves being a common factor. It is important for the valve to be compatible with the normal operating pressure — or working pressure — of the system. In addition, system designers need to ensure the system never exceeds the design pressure of the valve, which is its manufacturer-provided maximum pressure limit.
-
End connections: End connections are crucial to how well a valve will resist leaking. They include integral tube fittings, pipe threads, pipe flanges, welded ends and other options. Choosing the appropriate end connections for a valve that meet the pressure, temperature and size of a system will make installations easier and reduce the number of potential leaks (see Figure 5).
-
Delivery: Once the above factors have been considered, it’s important to ensure you can actually get your valves in hand. Look for suppliers that can source your valves on time, including specialty ones that may require more lead time.

Using the steps outlined in the STAMPED method will help system designers create safe, efficient fluid systems.