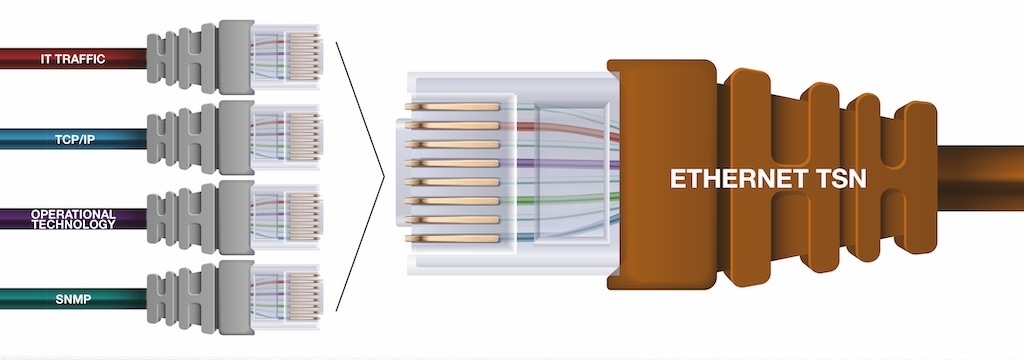
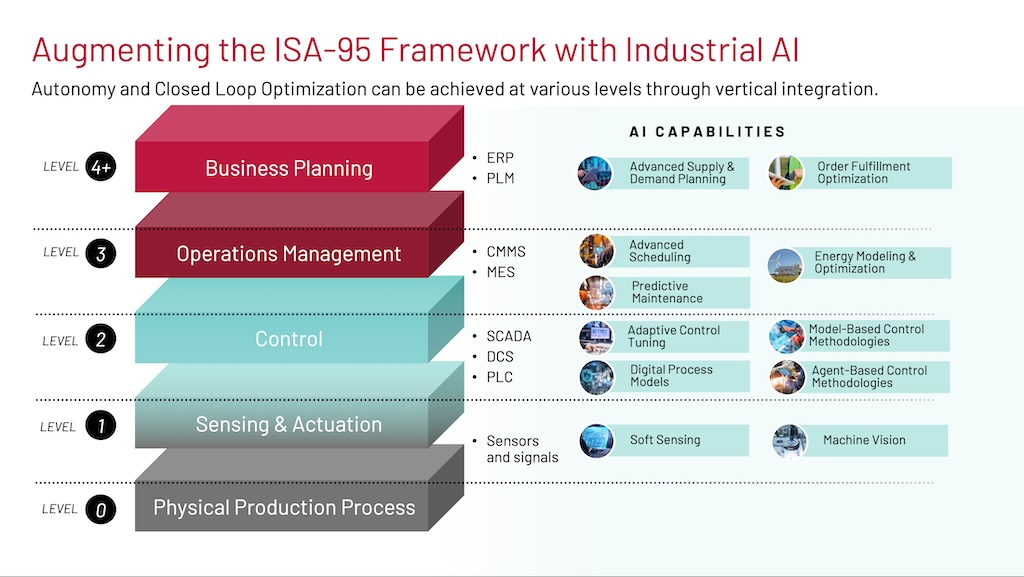
In 2025, manufacturing is expected to build upon industry 4.0’s emphasis on economic value, shifting the focus to a human-centric, sustainable and resilient approach. This article will explore what this shift means for the industry.

Industry 4.0 insights
- Discover how industry 4.0 innovations and a human-centric approach are shaping the future of manufacturing, with insights into sustainable practices, predictive maintenance and adaptive technologies.
- Explore the transformative power of AI, IoT and robotics in driving efficiency, resilience and sustainability, while empowering workers to make strategic decisions in a rapidly evolving industry.
When reflecting upon the past decade, it’s clear that industry 4.0 has been a key driver for manufacturing. Innovations in smart machines, internet of things (IoT) devices, robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), cloud and edge computing have advanced machines to operate more independently and provide human workers with timely insights needed to make decisions that boost efficiency, productivity and quality, while also reducing cost.
That said, as the industry evolves and faces growing unpredictability, embracing standardization and automation in manufacturing will be essential for future success.
In 2025, manufacturing is expected to build upon industry 4.0’s emphasis on economic value, shifting the focus to a human-centric, sustainable and resilient approach. This will ultimately help manufactures adjust to market changes and mitigate risk. Here’s what this means for the industry as a whole:
Industry 4.0 and humans
A human-centric focus involves workers in decision-making by providing timely insights. Machines will continue to take on more repetitive and dangerous tasks with greater intelligence and independence, thanks to AI, while collaborating with human workers, who will be freed up to take on more complex challenges and make strategic decisions.
For example, with predictive maintenance, previous industry 4.0 technology captured and analyzed data to provide dashboards with alerts and reports to human workers, who then assessed and made decisions on the appropriate actions. Now, those same workers are equipped with devices, such as augmented reality glasses, that immediately provide equipment health data, allowing real-time assessments to be made.
From there, workers can make strategic decisions and take corrective actions to mitigate production impact risks and challenges and respond quickly to changes that are needed to ensure optimal production.
How IIoT can impact sustainability
The shift from economic considerations to sustainable development in the face of global challenges, such as natural resource depletion and environmental decline, will be key. While the full scope of sustainability in manufacturing is still being understood, use of technologies like AI, robotics and the internet of things (IoT), are being explored in areas like optimizing water and energy usage, minimizing greenhouse carbon emission, pollution control and limiting waste through recycling and reuse.
An example of this is how energy consumption data via IoT sensors can now be monitored in real-time and operations environment settings can be strategically adjusted to dynamically optimize usage.
Resilient manufacturing with industry 4.0
Finally, the ability to be resilient enables manufacturers to quickly adjust and adapt to changes in the marketplace. The COVID-19 pandemic introduced unprecedented challenges that forced the world to rethink the way they worked to survive. Manufacturers had to pivot from using technology for specific issues or finite scopes to leveraging it for broader, more comprehensive solutions, like reshoring and distributed manufacturing from single locations.

The goal of this approach is to spread and diversify risk by establishing equal manufacturing capabilities globally, ensuring that any product can be manufactured in any factory at the lowest overall cost and highest efficiency.
Moving forward, expect manufacturers to take a more holistic view of manufacturing by shifting from a sole emphasis on economic value, to an approach that’s more human-centric, sustainable and resilient. Manufacturers who leverage the power of AI to accelerate automation in a nonsiloed, holistic way will be well poised to quickly adjust to market changes and mitigate risk effectively.
Supply chain and production will be seen as two sides of the same coin and the standardization of technologies and processes across all parts of the manufacturing process will be prioritized. Technologies like digital twins, collaborative robots, simulation and modeling, as well as generative AI, will play bigger roles in ushering in this new era as manufacturers work to ensure they’re ready for anything, regardless of what’s happening in the world.