Smart device and equipment manufacturers must include digital twins in their product roadmap to help their industrial customers digitize manufacturing operations
Learning Objectives
- Learn the fundamental aspects of digital twin technology in manufacturing.
- Understand the immediate benefits for smart device manufacturers of adopting intelligent digital twins.
- Identify how manufacturers can use digital twins in their product roadmap.
Digital twin insights
- Digital twins come in various types, including product twins, production twins and performance twins, which find applications in manufacturing, design optimization, process automation, predictive maintenance and informed decision-making.
- Immediate benefits of digital twin adoption include reduced product development time, improved product quality, enhanced training opportunities and improved sustainability.
In the not-so-distant past, digital twins in manufacturing were an obscure idea that barely made waves in the industry. So how has a concept that was so alien to us become one of the most talked about technological advancements recently?
According to a new market research report by MarketsandMarkets, the digital twin market by type and application (predictive maintenance and others) in terms of revenue, is expected to reach $73.5 billion by 2027, at the compound annual growth rate of 60.6%. And a McKinsey research indicates that 70% of C-suite technology executives of large enterprises are increasingly considering investing in digital twins.
What is a digital twin?
Digital twin is a virtual representation of physical object, system, process or person with data products at their core that are linked with live data from multiple sources.
See Table 1 for the different types of digital twin and their importance.
| Type of digital twin | Where is it used? | What is it? | What does it do? |
| Product twin
|
Manufacturing
|
Virtual representation of a product |
|
| Production twin | Manufacturing | Virtual representation of a manufacturing facility |
|
| Performance twin | General | Virtual representation of a physical system |
|
Table 1: Types of digital twins and their application in the manufacturing industry. Courtesy: Saviant Consulting
Digital twins as a critical enabler in digitizing manufacturing operations
Industrial enterprises continue to deploy smart devices and machines in their manufacturing facilities and client sites for fault-free operations and improved business efficiency. They need machines that deliver intelligence enabling them to control downtime and failures and maximize the equipment-useful life.
Digital twin is one such technology that enables industrial enterprises to gain real-time and predictive insights into machine health by creating a virtual replica of the entire factory, manufacturing facility or equipment. They enable the assessment of a product’s impact before it is manufactured and integrated with the existing systems, making manufacturing smarter.
Some immediate benefits of adopting intelligent digital twins in manufacturing include:
- Reduced product development time: Digital twins facilitate rapid design optimization, cutting down physical testing of each prototype. The products can be assessed before they are manufactured and integrated into the existing system. The digital twin technology has enabled companies to accelerate time-to-market by 50% while improving product quality by up to 25%.
- Improved quality and performance: Intelligent digital twins, when simulated through real-time data from multiple sources, can help detect any design flaws or product features that may lead to defects or quality issues. Further, this technology aids in predicting product performance in service, allowing teams to adjust design and functionality before production begins.
- Enhanced training opportunities: Digital twins help manufacturing companies train new employees without physical plant visits. While companies have been using simulations for workforce training, digital twin replicates real-world scenarios that give employees the training experience of a real-world setup. This technology helps grow their knowledge base in a safe environment.
- Improve sustainability: A digital twin can help improve product component traceability and reduce material consumption, which aids in sustainability. It allows companies to swap materials for more sustainable options and reduce scrap in the manufacturing process.
Smart device and equipment manufacturers must include digital twins
Customers are expecting businesses to provide digital twin enabled products. Especially if businesses deliver smart devices, machines and equipment to industrial enterprises.
What if businesses could deliver digital twin intelligence through the product hardware and software together? For this, the product needs advanced capabilities, starting by including digital twins into the product roadmap.
To keep it simple, businesses need to add intelligent digital twins to the product roadmap for:
- Future readiness: To become a part of large manufacturing processes, where it is required to diagnose the health of the machines using simulation or digital twins for factories or sites.
- Equipment useful life: To maintain machinery for years, and minimize downtime and by maintaining regulatory standards.
- Continuous improvement: At manufacturing sites, it’s imperative for industrial enterprises to improve operational efficiency.
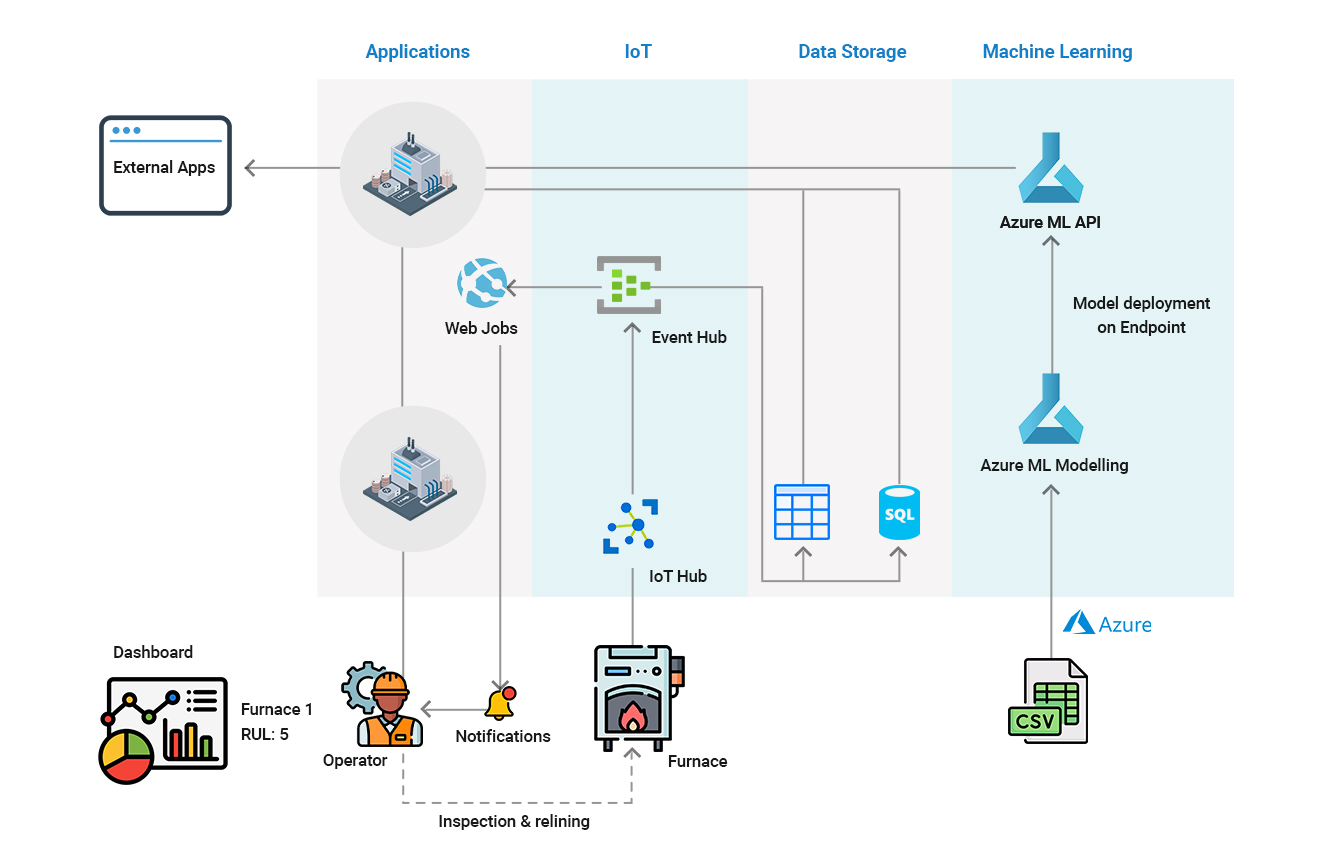
For an illustrative example, look at a large thermal processing equipment manufacturer. With a legacy of serving clients across 40 countries for the past 60 years, the manufacturer faced critical challenges, including expensive and time-consuming diagnostics of on-field equipment and complexity in managing equipment monitoring software for multiple customers.
To address these problems, the company partnered with Saviant Consulting to build a platform to create digital twins on Microsoft Azure for its customers’ melt shops. Saviant designed a multitenant, loosely coupled architecture to create this scalable platform, which helped reduce overheads while also managing multiple equipment for its customers.
The system was developed to gather and store equipment data over standard protocols for further analysis. All key performance indicators (quality, overall equipment effectiveness, throughput, etc.) of induction melting equipment are available anywhere, anytime, for the manufacturer’s customers, via a virtual view for proactive adjustments in production plans. The system also features intelligent capabilities predicting furnace lining health and advising site engineers on servicing and replacement times to prevent downtime, revenue loss or potential lawsuits.
Overall necessity of digital twins
Smart device, machine and equipment manufacturers should integrate digital twins into their product roadmap for creating intelligent, efficient industrial products. This move will enhance product quality, production efficiency and operational performance, not just for these manufacturers but also their industrial clients.


