Singapore’s manufacturing industry is facing a tough 2024, but it’s expected to recover in 2025 as semiconductors bounce back.
Semiconductor insights
- Singapore’s heavy reliance on semiconductor and high-tech industries caused a production slump, but recovery is expected by 2025.
- Limited space drives Singapore’s focus on high-margin, technologically advanced manufacturing, positioning it for strong growth post-2025.
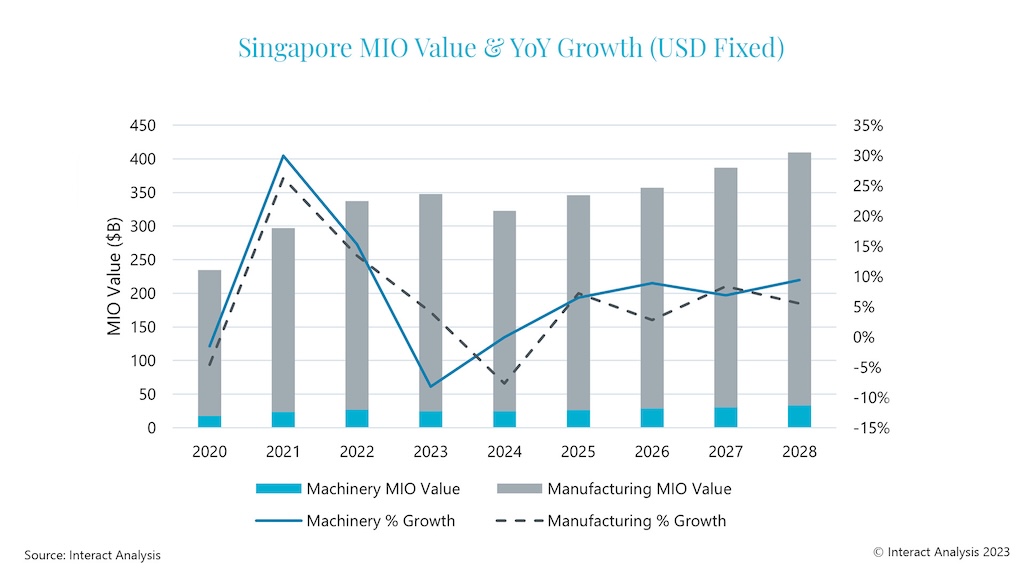
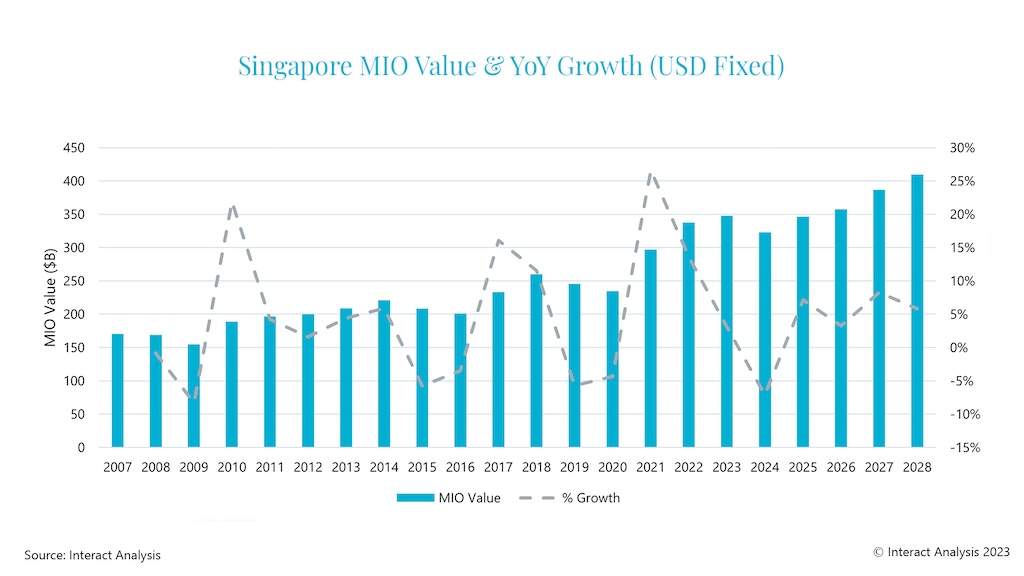
Singapore witnessed steep growth in its total production output over the past 15 years, almost doubling between 2007 and 2022, but has seen manufacturing output contract in 2023 and it is expected to slump further in 2024. We anticipate the production outlook will be gloomy in 2024, before bouncing back in 2025 as the global semiconductor market recovers from the current negativity.
In fact, Singapore’s economy as a whole has experienced a difficult 2023, with a slowdown in manufacturing output putting the brakes on, as the central bank continues to tackle persistently high inflation and interest rates remain high.
The city-state is the 11th addition to the Asia Tri-Region in Interact Analysis’ Manufacturing Industry Outlook (MIO) Tracker and we have been conducting in-depth analysis of its production output with historic data spanning 15 years, its current situation and its future outlook.
The city state has a heavily service-based economy with very little agriculture and around a quarter of its GDP comes from industrial operations. Manufacturing is a key pillar of its economic growth, while its business positive laws and regulations, and deepwater port have driven rapid growth over the last 15 years. Singapore is also the 5th largest machine producer in the Asia Tri-Region, with total machinery output of $27 billion in 2022.
Heavy reliance on semiconductors leading to current dip
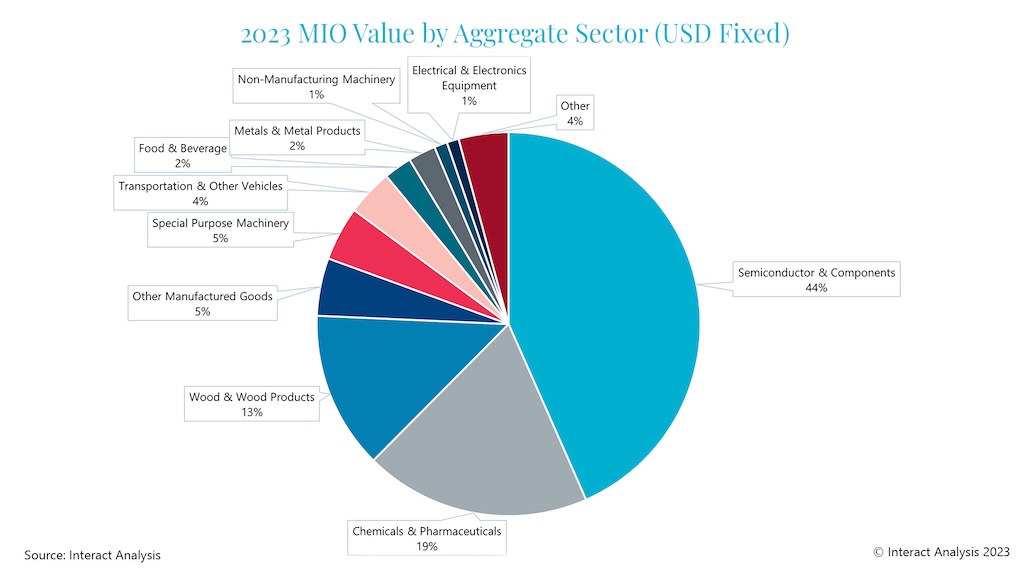
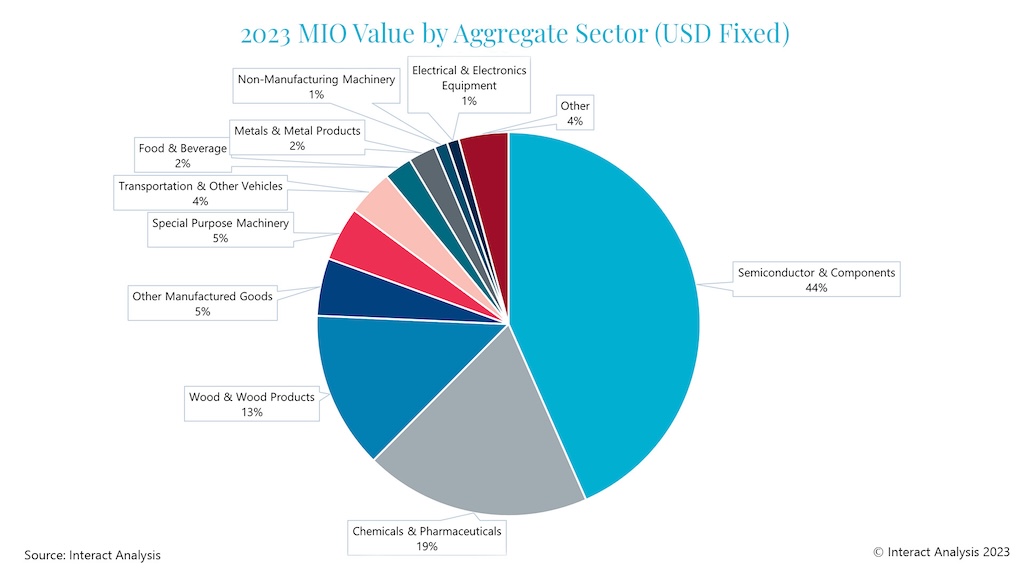
Singapore’s manufacturing sector is heavily reliant on specific industries, most notably semiconductors & electronic components, and chemicals & pharmaceuticals, accounting for 43.7% and 18% of total production, respectively. These are both technologically advanced industries with relatively small geographic footprints and high margins, and so ideally suited to Singapore.
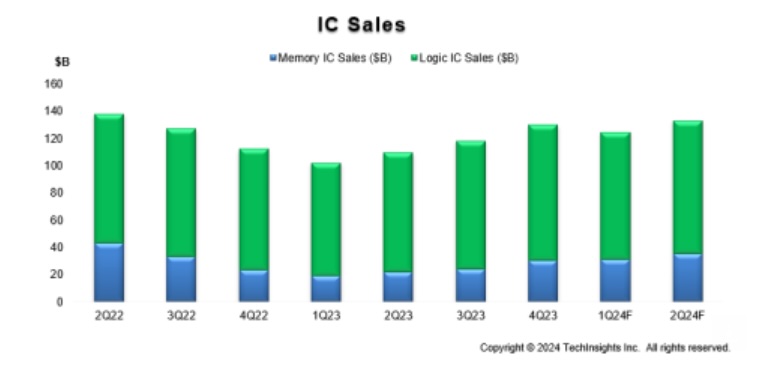
The current global semiconductor slump has hit Singapore’s production output hard and, because of the boom in semiconductors in recent years, the fall in demand this year looks particularly poor in percentage terms. However, the industry sector is expected to start its recovery next year, leading to a much stronger 2025 for the country’s manufacturing economy overall.
Limited space and business positive regulations attract high-margin manufacturing
Sitting between the Netherlands and Australia with a total MIO production value of around $200bn per year, Singapore is a sovereign island city-state about half the size of London, so limited space and high costs/wages mean manufacturers have to be very selective about what they produce as there is not enough space for large production sites.
In addition, many industrial machinery and automation companies have headquarters in Singapore but tend to have factories in neighbouring regions. Singapore has focused its manufacturing on hi-tech industries and on component production, such as gears, bearings, compressors and semiconductors, which requires less space and storage, compared to larger finished goods. Many of the machinery companies producing within Singapore are focused on components for larger machines.
Recovery from 2025 forecast, as Singapore’s growth outstrips China’s
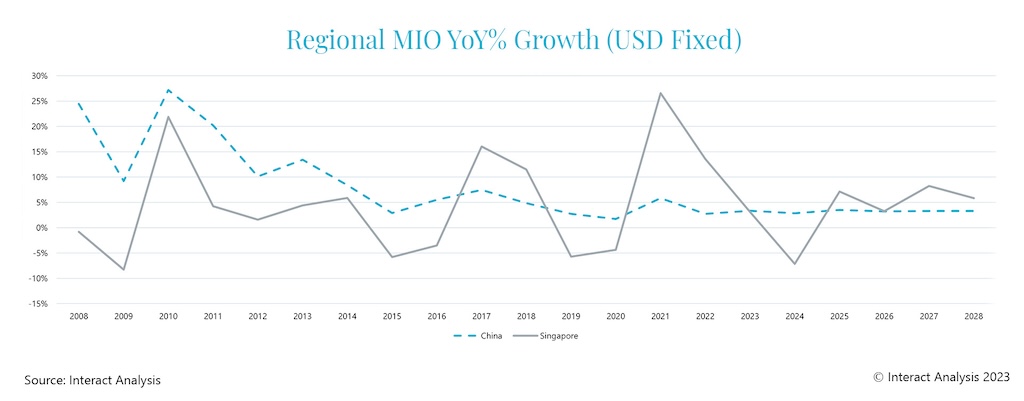
From 2025 out to 2028, we forecast continued growth for Singapore’s manufacturing output. From declines in 2023/24, it will recover strongly to become one of the Asia Pacific region’s best performers, outstripping China’s manufacturing output growth between 2025 and 2028. However, Singapore will need to monitor its over-reliance on particular industries carefully and will remain inextricably linked to the fortunes of the global semiconductor industry for the foreseeable future.
Produced by analysts around the world, Interact Analysis’ Manufacturing Industry Output (MIO) Tracker now covers 45 countries. It is published every quarter and provides a crucial insight into over 102 industries and sub-industries, presenting 15 years of historical data alongside a 5-year forecast and unparalleled analysis of the global machinery and manufacturing industry.
– Interact Analysis is a CFE Media and Technology content partner.