Realizing the benefits of automation in an industrial setting requires significant upfront investment. Software must be modernized and data must be migrated to the hybrid cloud.

Learning Objectives
- See how artificial intelligence can scale to meet industrial automation challenges.
- Realize greater safety and efficiency through industrial automation cloud applications.
- Learn how to realize benefits from industrial automation as part of Industry 4.0.
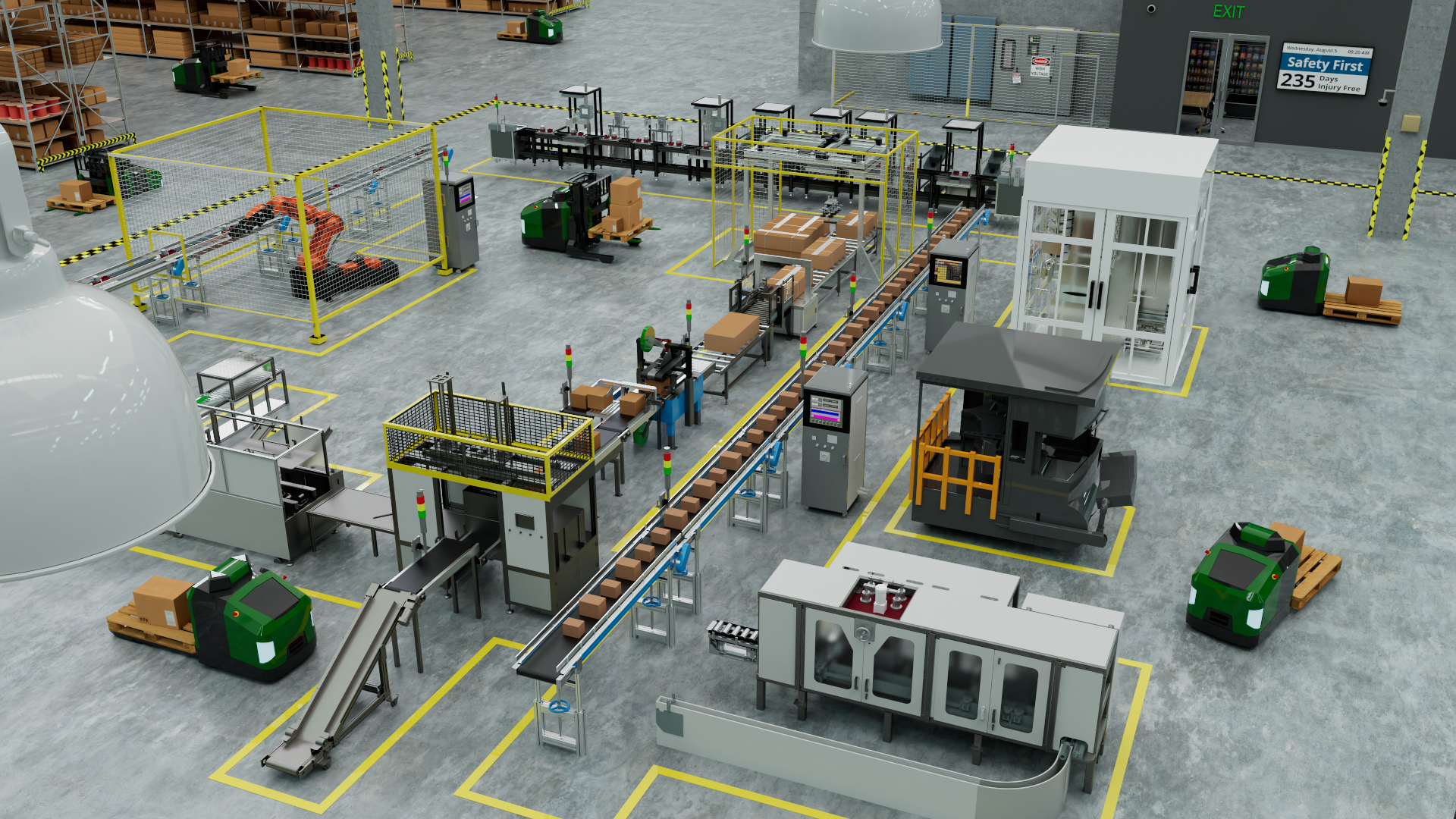
Automation has the potential to reduce costs, save time, increase productivity and also help keep employees safe. By some estimates, utilities can reclaim up to 50% of their time through the thoughtful application of automation techniques. But particularly in an industrial context, applying automation at scale requires having the right digital infrastructure, one capable of harnessing massive troves of data and running advanced artificial intelligence (AI) where and when needed.
The industrial automation promised by Industry 4.0 boils down to three important components:
- The ability to gather and store vast and changing amounts of data
- The ability to run models or other software on top of that data in almost any location
- The ability to direct action from the insights identified by the models.
Companies need a digital infrastructure footprint that stretches from the edge to the data center and the cloud. The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) that gathers data, the AI that analyzes and automates using data, and the hybrid cloud infrastructure that connects systems together with automation and workflow – these are the building blocks for Industry 4.0.
Meeting industrial automation challenges at scale
When it comes to scaling AI for industrial automation, a few key challenges arise. The amount of data to be processed grows exponentially as the organization works to capture all the information necessary for AI to make decisions. The AI models needed for analyzing the data at scale also get correspondingly more complex.
Most importantly, there is a need for real-time decision making and direction on the floor and in the field, meaning operational data and software to use it need to be accessible anywhere. Visual inspection AI is capable of automating a vast array of tasks, for example by using image data from a video feed or mobile phone to identify flaws in products or machinery or compliance issues, like when employees unknowingly enter unsafe areas. However, for the insights of these models to be useful, interventions need to be able to happen fast, not after the image in question has been sent to a data center for analysis. By then, the damage will have been done.
These needs underscore the importance of a hybrid cloud architecture in managing industrial automation at scale. Hybrid cloud can provide a common container-based platform across all infrastructure locations, the ability to auto-scale based on workloads and the flexibility to run the platform and access data in any cloud – public, private or at the edge. It also provides the ability to manage hybrid cloud infrastructure from one control plane, deploying software updates and security patches to the entire organization with ease.
Greater safety and efficiency through industrial automation
With the right digital infrastructure, employees in an industrial setting can be safer and more productive. Companies can begin to deploy location management solutions that help organizations automate maintenance and support processes and improve visitor and workforce safety. Technicians can take advantage of point-and-click capabilities, easily deployed with no-code approaches, that seamlessly integrate with legacy software which reduces overall reliance on information technology (IT) staff. Workforce mapping and asset visualization tools can be used to optimize travel routes of field technicians. Real-time monitoring enables scheduling and dispatching adjustments based on actual service call progress. By automating certain elements of the asset management process, equipment can be safer, more reliable and easier to repair when maintenance is needed.
Automation is even starting to be used to remove employees from harm’s way. By using drones to gather image data for vegetation management and equipment inspections, and visual inspection AI to monitor the image data for issues, there’s less need to send technicians, arborists and line workers into more dangerous scenarios, like transition towers and scaffolding, in the first place. By far, the strongest case for automation exists in scenarios where workers may be unsafe.
How to realize benefits from industrial automation
Realizing the benefits of automation in an industrial setting requires significant upfront investment. Software must be modernized and data must be migrated to the hybrid cloud. This can be a tedious process. Depending on the size of the organization, there may be countless terabytes of data to break into components and migrate. However, the benefits vastly outweigh the costs. Legacy software cannot deliver on scalable automation, because it cannot be run where needed, it cannot make all data available where needed, and it cannot run sophisticated AI through a smartphone. With a hybrid cloud infrastructure, all of these capabilities become available. Users can deploy IIoT in the field to gather data and design models to automate using that data. Users can run models wherever and whenever needed.
Joe Berti is VP product management, AI applications, with IBM Cloud and Cognitive Software. IBM is a CFE Media content partner. Edited by Chris Vavra, web content manager, Control Engineering, CFE Media and Technology, [email protected].