Emphasizing the critical importance of proper personal protective equipment (PPE) in safeguarding workers from the risks of arc flash events is critical.

Learning Objectives
- Learn three important factors for arc flash and shock hazard labels in high voltage electrical panels.
- Understanding the break-down of arc flash equipment.
- Learn best practices for maintenance and inspections of arc flash PPE.
Arc flash PPE insights
- Arc flash incidents can happen in diverse workplaces, necessitating proper personal protective equipment (PPE) selection crucial for safeguarding workers from potential serious harm.
- Utilizing specific standards, regular equipment inspections, diverse gear sizes, and fostering safety culture are pivotal in ensuring effective arc flash protection.
When thinking about personal protective equipment (PPE) used for arc flash protection, many would first imagine it being used in a high voltage setting such as a substation or generation facility. The truth is given the right conditions, an arc flash event can occur inside any business. Selecting the right arc flash PPE is critical for keeping workers safe who are exposed to electrical hazards. Without a good process, an arc flash event can cause serious injury or death. Therefore, taking note of a process to get the right equipment helps ensure a safer workplace.

Understanding three important PPE factors
Arc flash PPE requirements are difficult to navigate if the information is not readily available. To start, you can often find this information displayed in a high-voltage electrical panel. The arc flash and shock hazard label outlines three important factors:
-
Working distance – Refers to the distance between the person’s head and chest area from the potential arc source.
-
Incident energy – Measured in calories per square centimeter (Cal/Cm^2) which is the amount of thermal energy exerted on a surface, positioned a specified distance from the source, produced during an electrical arc event.
-
Arc flash boundary – The distance at which a person without PPE may get a second-degree burn from an arc flash occurrence.
If the above information is unavailable on the arc flash equipment, it is recommended an arc flash hazard and risk assessment is conducted to establish the incident energy and boundary at a specific location. This can be completed by consulting an electrical engineer to perform the analysis or using software tools that calculate arc flash energy and working distance.
Using standards for verification
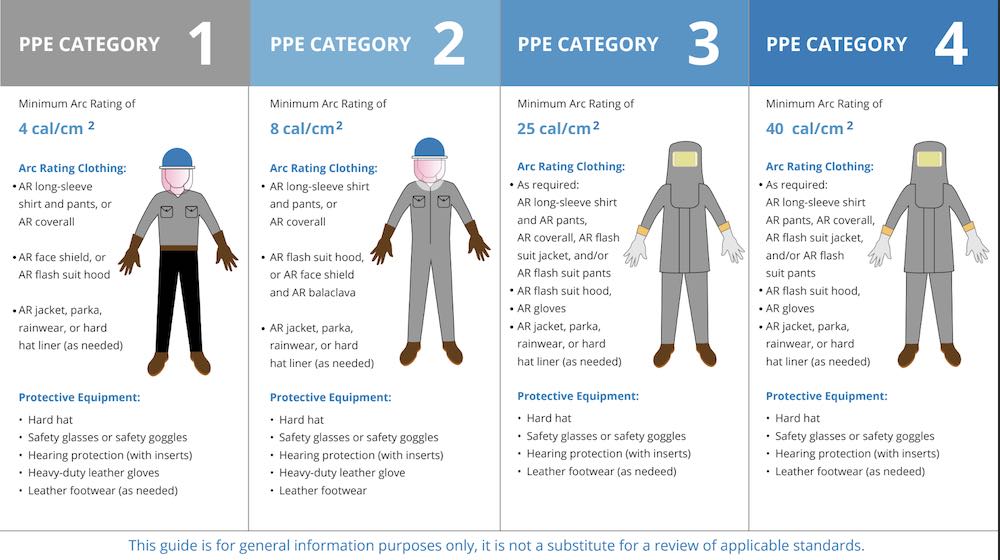
With those three pieces of information, verify them using relevant standards such as NFPA 70 (America), CSA Z462-21 (Canada) or IEEE 1584. These standards will support the decision in selecting PPE based on the incident energy levels.
For example, using CSA Z462-21 incident energy analysis will provide insight into the appropriate PPE from Table 3, 6A, and 6B. Once the PPE category is determined, refer to Table 6C which outlines the required PPE to be used.
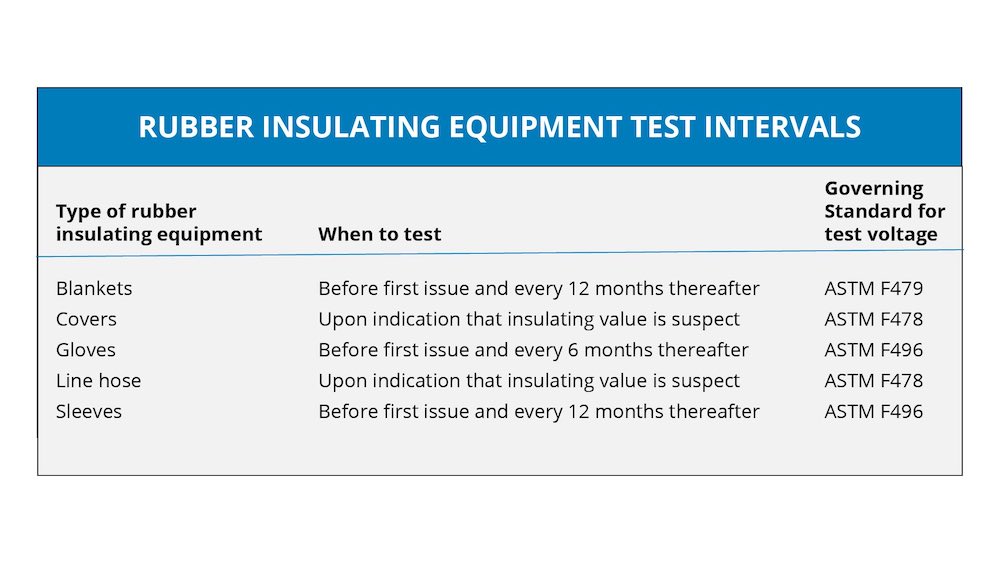
Prioritize buying arc flash gear that provides an acceptable fit for every team member. It’s pivotal to invest in multiple sizes because loose or tight-fitting equipment can become a safety risk. It is recommended all workers using arc flash PPE should have their own pair of flame-resistant coveralls, balaclava, approved safety footwear, safety glasses and hearing protection. Inspecting these items should become part of the regular maintenance routine to identify any potential risks. For example, parts of the arc flash equipment have a shelf life which requires inspection.

Arc flash PPE best practices
It is recommended an inspection checklist is filled out before each use of arc flash PPE and other isolated equipment. Like fall protection requirements, If any damage is spotted, employees should tag it, remove the PPE from service, and report it to management.
Training is another crucial factor. Ensure the team follows a detailed and regular training schedule to educate on the hazards associated with arc flash and how to properly use the equipment. This is a good place to revisit the equipment selection criteria, especially after there has been any upgrades or changes to the electrical system.
Lastly, fostering a company culture towards safety can greatly improve employee safety. Each person is their own safety critic and having safe operations top of mind is going to mitigate the risk of serious injury or death on any job site.



