Companies looking to take their automation game to the next level also need solutions that can help them maximize efficiency and address maintenance concerns before they happen.

Learning Objectives
- Understand how predictive maintenance (PdM) can help companies gain a competitive advantage.
- Learn how to develop a three-phase implementation approach.
- Learn about the benefits advanced PdM can provide companies.
Predictive maintenance insights
- Predictive maintenance (PdM) shifts from reactive fixes to proactive interventions, utilizing real-time data and analytics to prevent equipment failures and optimize operations.
- Implementing PdM involves phased approaches, from leveraging existing sensors to integrating robust networks and advanced analytics, enhancing reliability, safety, and efficiency.
From robotics to control systems, advanced sensors and the industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), there are a wide range of solutions that manufacturers can utilize to improve automation. However, manufacturers looking to take their automation game to the next level also need solutions that maximize efficiency and address maintenance concerns.
In the never-ending effort to minimize downtime, industrial manufacturers are adopting predictive maintenance (PdM) strategies to increase the reliability and extend the life of equipment. By leveraging the growing power of data, sensors and advanced analytics, PdM transitions from traditional reactive maintenance to predicting and preventing failures before they occur.
Understanding predictive maintenance’s role in manufacturing
Equipment maintenance traditionally followed a reactive model and addressed failures after they occurred. This reactive approach often resulted in downtime, production disruptions and safety hazards. As they recognized the limitations of this strategy, manufacturers adopted preventive maintenance, where equipment is serviced at predetermined intervals, regardless of its actual condition. While preventive maintenance offered significant improvements, it still lacked the precision and efficiency needed to optimize operations.
Enter PdM, which is a data-driven approach that leverages the power of connected digital factories. By continuously monitoring equipment through sensors and smart devices, PdM gathers real-time data on various parameters like temperature, vibration and performance. This data is then analyzed using sophisticated algorithms and machine learning models to predict potential failures before they occur. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions, preventing breakdowns and ensuring smooth production processes.

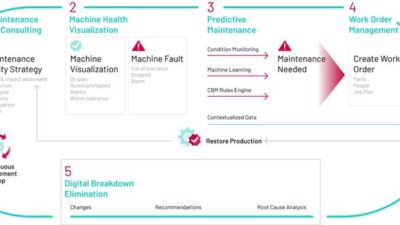
Developing a three-phase implementation approach
While the benefits of PdM are undeniable, its implementation can vary depending on an organization’s current infrastructure and resources. Even manufacturers deep into their automation journey may need to implement PdM in a series of smaller steps. This phased approach can help manufacturers of all sizes embark on a successful PdM journey.
Phase 1: Integrate existing smart devices
The first step in PdM doesn’t require extensive investment. Most modern equipment comes with built-in sensors that generate real-time data on performance, temperature, vibration and other critical parameters. This data is the lifeblood of PdM, providing the raw material for analysis and prediction.
Manufacturers that utilize these resources can gain valuable insights into equipment health and identify potential issues early on. This low-hanging fruit provides a solid foundation for further advancement. Some companies, depending on their current level of automation, may already be doing this.
Phase 2: Create robust network infrastructure
Any manufacturer that has implemented IIoT, robotics or any other smart system already knows the importance of a strong and resilient network infrastructure. The same is true for those looking to incorporate PdM.
Taking a more comprehensive approach to PdM includes adding dedicated sensors and tying all the data together for in-depth analysis. A robust network infrastructure is essential for collecting and transmitting data from sensors to a central location for analysis. Secure cloud-based solutions are becoming more popular for data storage and accessibility.
For organizations wanting to create a sophisticated PdM program, pre-configured solutions offer a cost-effective entry point. These solutions often combine sensors, software and data analysis tools tailored for specific equipment types or applications. They provide actionable insights and maintenance recommendations, empowering personnel to take preventive measures and avoid expensive downtime. Vendors also can be a good source of guidance on future-proofing infrastructure choices.
Manufacturers also should consider investing in connected infrastructure today even if they haven’t fully explored leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in their PdM programs yet. Building the data capacity will ensure they are prepared for the future integration of these powerful technologies.
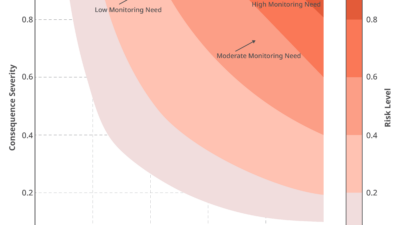
One note of caution: Analyzing vast amounts of data without proper historical context can be overwhelming. As manufacturers ramp up PdM, they should focus on critical assets and equipment first before expanding the program as data collection and analysis capabilities mature.
Phase 3: Build a foundation for advanced analytics
As their data collection efforts and expertise grow, organizations can begin leveraging AI and machine learning to analyze vast amounts of historical data, identifying subtle patterns and correlations that predict not just equipment failures but also performance degradation and anomalies. With a robust data infrastructure coupled with AI, manufacturers can enable the development of customized and sophisticated predictive maintenance models. This can be a natural add-on for those already utilizing these solutions as part of their automation initiatives.

Five benefits of advanced PdM
The journey from basic PdM to advanced predictive analytics is a transformative one. By adopting a phased approach and aligning technology investments with future needs, manufacturers can unlock:
-
Enhanced reliability. PdM minimizes downtime and production losses by anticipating and preventing equipment failures, ensuring uninterrupted production and improved operational efficiency.
-
Extended equipment life. PdM helps prevent unnecessary wear and tear, extending the lifespan of valuable equipment.
-
Improved safety. Early detection of potential hazards minimizes the risk of equipment failures leading to accidents or injuries.
-
Optimized performance. PdM provides valuable real-time and long-term insights into equipment performance, enabling data-driven decisions to optimize manufacturing processes and improve overall factory efficiency.
-
Reduced maintenance costs. By shifting from reactive to proactive maintenance, PdM avoids the need for emergency repairs, leading to significant cost savings.
Predictive maintenance’s future
The future of PdM is bright. Continuous advancements in sensor technology, data analytics, and AI will further enhance its capabilities. In the coming years, manufacturers can expect to see:
-
More sophisticated predictive models. AI will play a bigger role in developing accurate and context-aware models that can predict not just failures but also performance degradation and anomalies.
-
Self-learning and adaptive systems. PdM systems will learn and adapt over time, refining their predictions and recommendations based on new data and changing operating conditions.
-
Integration with other systems. PdM will integrate with other operational technology and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, creating a holistic view of production processes and enabling real-time decision-making.
-
Maintenance in the moment. As PdM grows more sophisticated, monitoring and the latest insights will be accessible via mobile devices, empowering maintenance personnel to make real-time adjustments before issues arise.
Developing a competitive edge with predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance has the power to transform industrial operations for the better. By embracing a phased implementation approach and building the necessary foundation for advanced analytics, manufacturers can unlock its immense potential.
The journey to PdM success is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Organizations can start by first identifying specific needs and pain points. From there, they can choose the entry point that best aligns with their resources and goals.
By realizing significant equipment reliability, operational efficiency, safety and cost benefits, organizations that adopt a sophisticated, data-driven approach to predictive maintenance can level up their automation efforts and secure a competitive advantage in the ever-evolving industrial landscape.