Larger payload collaborative robot, artificial intelligence (AI)-enhanced robotics, laboratory-robotics integration, robotic order fulfillment, and virtual reality robotic software were among advances at Pack Expo 2021 Las Vegas.

Learning Objectives
- Learn about ABB GoFa higher payload collaborative robot, and integrated AI robotic solutions.
- Examine laboratory centrifuge assistant and flexible omnichannel order fulfillment.
- See new features of ABB RobotStudio for virtual reality and augmented reality.
A heavier payload collaborative robot, robotics enabled by artificial intelligence, and laboratory robotic integration were among announcements from ABB Robotics at Pack Expo Las Vegas 2021.
The ABB 6-axis GoFa CRB 15000 robot supports the growing demand for a collaborative robot capable of handling heavier payloads to enhance productivity and flexibility. ABB’s partnership with Covariant is bringing bring AI-enabled robotics solutions to accelerate ABB’s expansion into the distribution and e-commerce sectors. ABB Robotics is developing technologies to assist and automate clinical pathology laboratories and other standard hospital processes, and the Centrifuge Assistant is ABB Robotics first pipeline product for the healthcare industry; it integrates the Single-arm YuMi (SAY) cobot with a centrifuge.
Other developments included robotic order fulfillment and virtual reality robotic software.
ABB GoFa higher payload collaborative robot, safety features
The ABB 6-axis GoFa CRB 15000 robot supports the growing demand for a collaborative robot capable of handling heavier payloads to enhance productivity and flexibility. It is designed to work continuously alongside humans and be easy to install and use, GoFa will help businesses automate processes involving heavier loads and longer reaches to assist workers with repetitive and ergonomically challenging tasks.
With a reach of 950mm (best in class according to the September introductory information from ABB), it offers speeds up to 2.2 meters per second for collaborative tasks up to 5 kg. GoFa offers an effective solution for a variety of packaging applications, including pick, pack-and-place, kitting, product handling and more.
GoFa incorporates a range of features that allow it to be used alongside human workers without the space and expense associated with physical barriers or fences. Enabling a robot and human to share the same workspace and cooperate on the same tasks, without jeopardizing speed and safety, allows for maximum flexibility and efficiency.
GoFa features intelligent torque and position sensors in each of its six joints to offer superior power and force limiting performance. These joints eliminate the risk of injury to human workers by sensing unexpected contact between the cobot’s arm and a human to bring the robot arm to a stop within milliseconds.
Users can program GoFa via lead-through programming and ABB’s new Wizard easy programming software. Based on simple graphical blocks, Wizard makes it easy for non-specialists to automate their applications. The blocks represent actions such as move to location, pick up an object, and repeat task, making it easy and intuitive to build a series of simple processes for the robot to perform.
Robot users also can use ABB’s Rapid programming language supported by Robot-Studio.
Every ABB cobot installation includes a start-up package that provides ABB Ability condition monitoring and diagnostics and a support hotline, free for the first six months, to access ABB’s expert technical assistance, which is offering support across all industry segments.
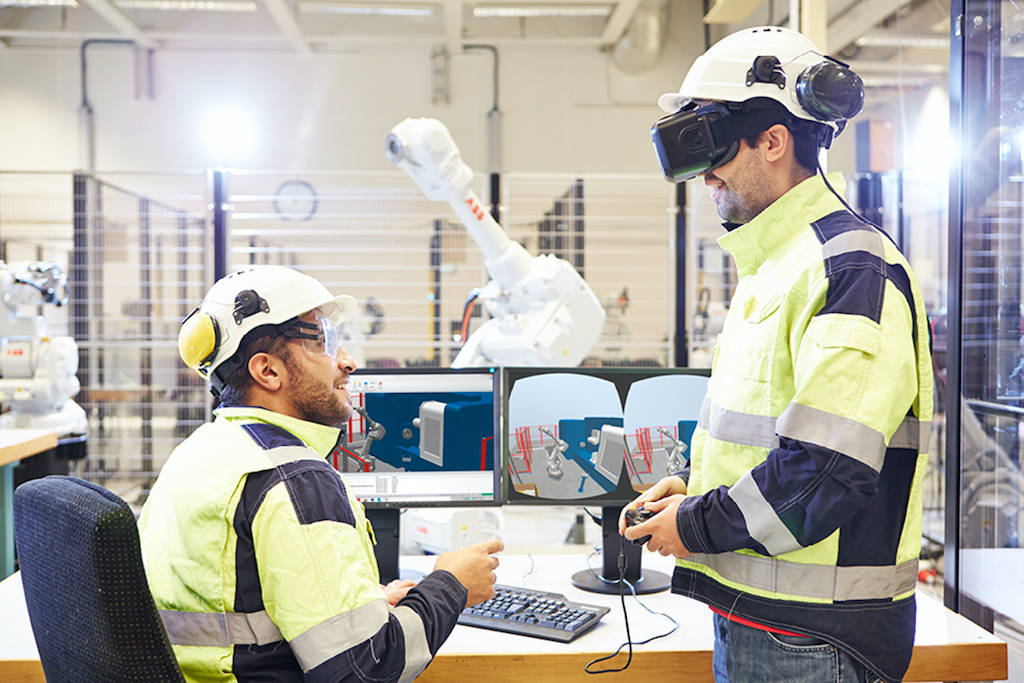

Integrated AI robotic solutions: the ABB IRB 1300 and Covariant
ABB partnered with Covariant to bring artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled robotics solutions to accelerate ABB’s expansion into the distribution and e-commerce sectors with fully autonomous warehouse order fulfilment solutions.
The companies share a vision for robotics enabled by AI, where intelligent robots work alongside humans in dynamic environments, collectively learning and improving with every completed task.
The growing demand for e-commerce fulfilment services and the complex and labor-intensive nature of the process offers unique potential for intelligent automation.
Today, warehouse operations are labor intensive, and the industry struggles to find and retain employees for picking and packing. Robots are ideally suited to repetitive tasks. Until now, they lacked the intelligence to identify and handle tens of thousands of constantly changing products in a typical dynamic warehouse operation.
Attributes that each company bring to the partnership include the following.
Covariant:
- The Covariant Brain is a universal AI that allows robots to see, reason and act in the world around them, completing tasks too complex and varied for traditional programmed robots.
- Covariant’s software enables robots to engage in reinforcement learning: adapting to new tasks on their own through trial and error and therefore constantly broadening the range of objects they can pick.
- The robust Covariant AI solution is capable of supporting autonomous materials handling, enabling robots to handle items of infinite variety.
The ABB IRB 1300:
- Combining the IRB 1300 with AI provides robust and smart options for customers in the food and beverage, ecommerce and logistics sectors.
- The compact IRB 1300 has a footprint that is 83% smaller and cycle times that are 27% shorter – allowing deployment in confined spaces and increasing productivity.
- It offers a variety of payload and reach options. It is the ideal solution to ensure fast and efficient picking and packing in food and beverage and logistics applications as it can pick different size parcels, cartoons and boxes from high-speed systems.
Laboratory centrifuge assistant: Single-arm YuMi Collaborative Robot
ABB Robotics is actively developing technologies to assist and automate clinical pathology laboratories and other standard hospital processes.
The Centrifuge Assistant is ABB Robotics’ first pipeline product for the healthcare industry. It’s currently in development and combines the Single-arm YuMi (SAY) cobot with a centrifuge to process phlebotomy tubes of up to 16mm in diameter.
The SAY Robot is a compact, lightweight (9.5 kg) instrument with the dexterity to interface with a laboratory centrifuge. It works by scanning a sample barcode and loading and unloading phlebotomy tubes, one-by-one using the robot arm. After the tubes are centrifuged, the robot unloads and sorts all of the tubes out of the inserts, putting them into the respective downstream outgoing test tube racks.
The Centrifuge Assistant is designed to automate standard medical or hospital laboratory process with the goal of reducing manual repetitive tasks and is being designed to work alongside medical technicians and laboratory personnel.
ABB Healthcare is in the process of developing technologies to automate clinical pathology laboratories as well as other standard hospital processes. The Centrifuge Assistant is ABB Healthcare’s first pipeline product. The Single-arm YuMi Robot has the dexterity to interface with a laboratory centrifuge.
Flexible omnichannel order fulfillment
A high-speed, high-variation robotic sorting and on-demand order picking digital simulation featuring ABB delta robots, PickMaster Twin software and the B&R AcopoStrak.
The growth of omnichannel retailing means distribution centers and logistics warehouses need to transform their systems to handle both pallets and packaging destined for retail shelves, while picking and packing highly varied items for shipping direct to individual consumers.
A significant driver for change has been the growth of direct-to-consumer (D2C) and direct-to-store (D2S) shipping, which is dramatically changing the way that consumers order and collect products.
Consumer goods manufacturers need the right infrastructure for maximum flexibility that can pick and handle a wide variety of goods in the widest range of combinations and in the shortest possible time.
The ABB Delta Robot, IRB 390 FlexPacker, faster, higher payload and more flexible delta robot to support customized packaging, vertical packing and high-speed, high-variation sorting and on demand order picking in logistics and e-commerce fulfillment centers. The IRB 390 FlexPacker robot is available as a four and five axis variant delta robot. It is 35% faster than the IRB 360-8/1130 FlexPicker, with a 45% increase in reachable volume and payload of up to 15 kg.
RobotStudio with virtual reality and augmented reality
Offline programming is the best way to maximize return on investment for robot systems. ABB’s simulation and offline programming software, RobotStudio, allows robot programming to be done on a PC in the office without shutting down production, allowing users to perform tasks such as training, programming, and optimization without production disturbance.
The tool is built on the ABB Virtual Controller, an exact copy of the real software that runs robots in production. This allows very realistic simulations to be performed, using real robot pro-grams and configuration files identical to those used on the shop floor.
- Picking PowerPac is used to simulate advanced picking and packing systems. This is a RobotStudio add-in with functionality that enables 3D simulation of multi-robot picking or packing systems. A technician can quickly create a simulation with real cycle times based on actual product flows with 1-10 robots and up to 4 conveyors.
- Palletizing PowerPac is used to simulate advanced palletizing systems. This is another RobotStudio add-in with functionality that enables 3D simulation of palletizing systems. An easy-to-use interface is designed around the palletizing process making quick work of ac-curate cycle times, pallet patterns and reach limits. Then run it on the real robot when it is ready.
- Logistic and warehouse applications can also be simulated using RobotStudio. This includes item picking, depalletize, and storage/retrieval systems.
ABB Ability connected services, data collector
Components of ABB Ability enable users to remotely monitor, troubleshoot, backup and optimize individual and fleets of robots for maximum availability, optimal maintenance and minimal total cost of ownership. All ABB robots come ready to be connected to ABB Ability Connected Services, wirelessly or hard-wired, unlocking a world of possibilities in predictive, proactive and immediate support, anytime, anyplace. Two major components of ABB Ability are:
- Connected Services 2.0: A cloud-based service suite that can help users drive performance and productivity improvements, thus saving maintenance and production costs quickly.
- Digital Factory Data Collector: A powerful local tool that does not require a connection to the cloud or a remote server. It allows users to store and organize valuable production data cross all robots within a company, across one or more facilities.
These tools enable customers to securely integrate and aggregate their data, combine with wider industry data, apply predictive analytics, and generate insights that can help them drive performance and productivity improvements.
Edited by Mark T. Hoske, content manager, Control Engineering, CFE Media and Technology, [email protected].
KEYWORDS: Collaborative robotics, robotic order fulfillment
CONSIDER THIS
How are robotics helping competitiveness?