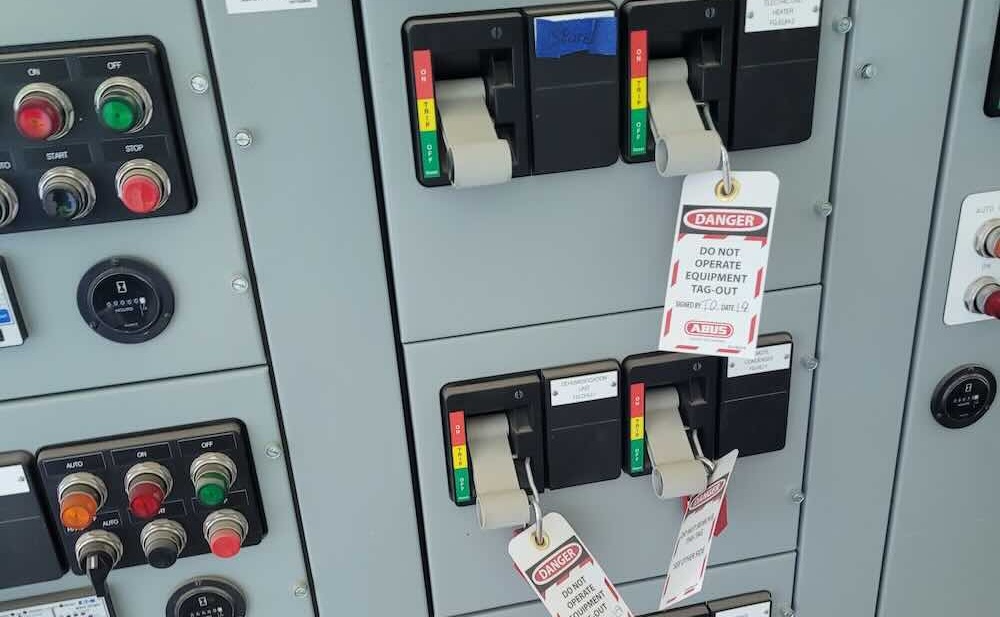
Absence of voltage testing is a hot topic among safety experts and electrical safety manufacturers and permanent electrical safety devices (PESDs) can help improve safety.

Absence of Voltage Testing Insights
- Permanent electrical safety devices (PESDs) are designed to improve overall safety and productivity in facilities.
- Absence of voltage testing is a hot topic among safety experts and electrical safety product manufacturers right now.
One of the most innovative product lines that Grace Technologies manufacturers are permanent electrical safety devices (PESDs). These devices have been distributed in industries around the world to improve overall safety and productivity. PESDs are permanently mounted and allow electricians to validate energy presence with voltage indicators and absence with the safe-test point and voltage test station. Here’s a quick look at how PESDs can improve your interactions around voltage through safety-by-design.
Voltage indicators provide a consistent reliable presence of voltage indication with their LED lights. However, when the equipment connected to the indicator is turned off, the LED lights go out as well. It should be noted that this indication is not a compliant method for verifying absence of voltage. Additional steps must be taken before an electrician or maintenance personnel is going open a cabinet that has been de-energized. That’s where the safe-test point and voltage test station PESDs come into play.
These absence of voltage testing PESDs allow qualified personnel to take a metered test at the test points while standing safely outside of the electrical equipment. The end result has proven to create a safer working environment time and time again. Using PESDs to test for absence of voltage through high-impedance-protected test points will always put your personnel on the safe side of controlling hazardous energy.
Absence of voltage testing is a hot topic among safety experts and electrical safety product manufacturers right now. This comes in the wake of a recent revision to NFPA 70E with Exception No. 1 of Article 120.5 (7). This Exception, based within the Control of Hazardous Energy standard, has been wildly speculated upon and has caused quite a stir in its true interpretation when it comes to application. We have a few folks at Grace with decades of experience in this sector who have helped pull together the clearest interpretation of what exactly Exception No. 1 means for Absence of Voltage Testing and GracePESDs.
Exception No. 1 states: An adequately rated permanently mounted test device shall be permitted to be used to verify the absence of voltage of the conductors or circuit parts at the work location, provided it meets all the following requirements:
- It is permanently mounted and installed in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions and tests the conductors and circuit parts at the point of work
- It is listed and labeled for the purpose of verifying absence of voltage
- It tests each phase conductor or circuit part both phase-to-phase and phase-to-ground
- The test device is verified as operating satisfactorily on any known voltage source before and after verifying the absence of voltage.
– Grace Technologies is a CFE Media and Technology content partner.